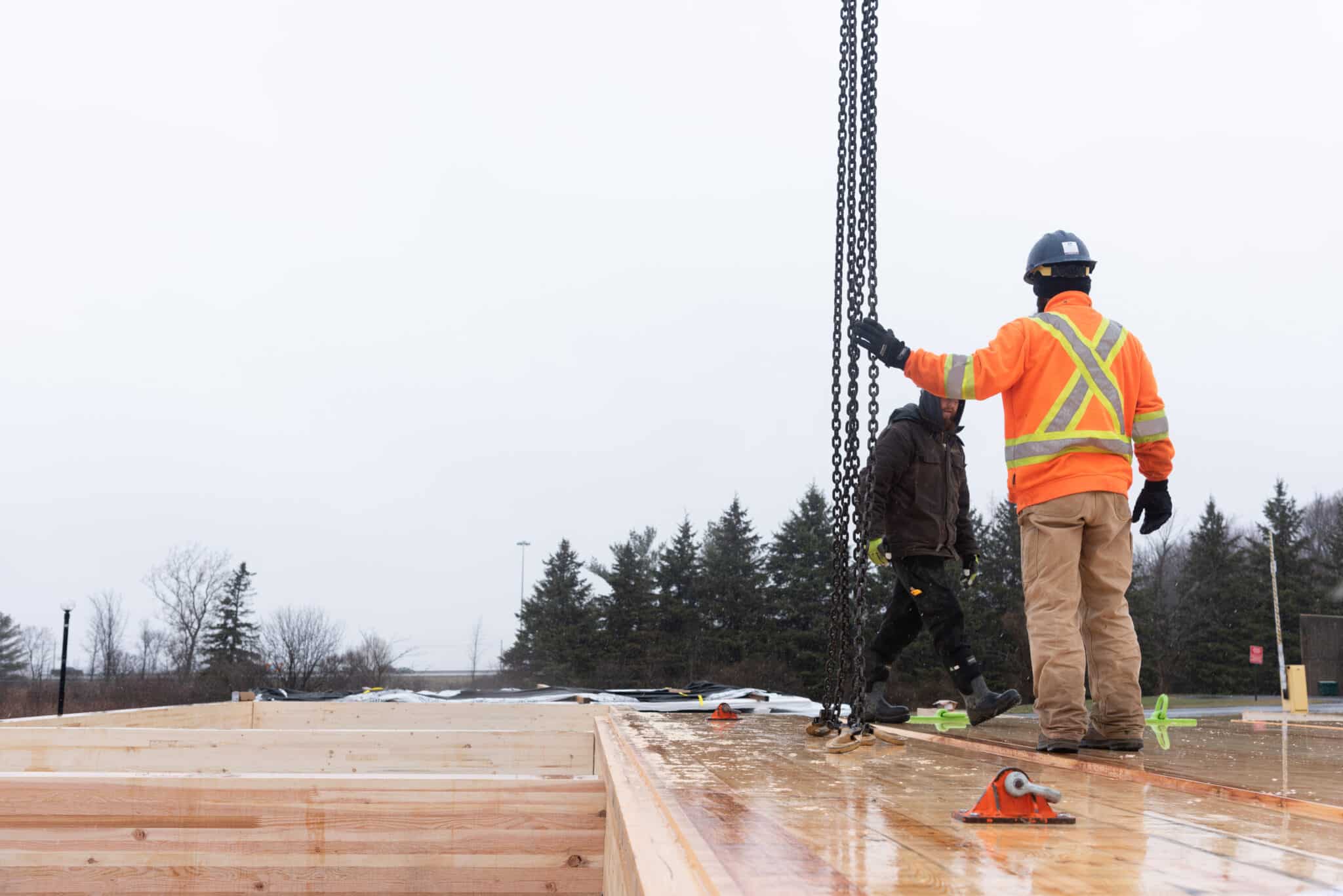
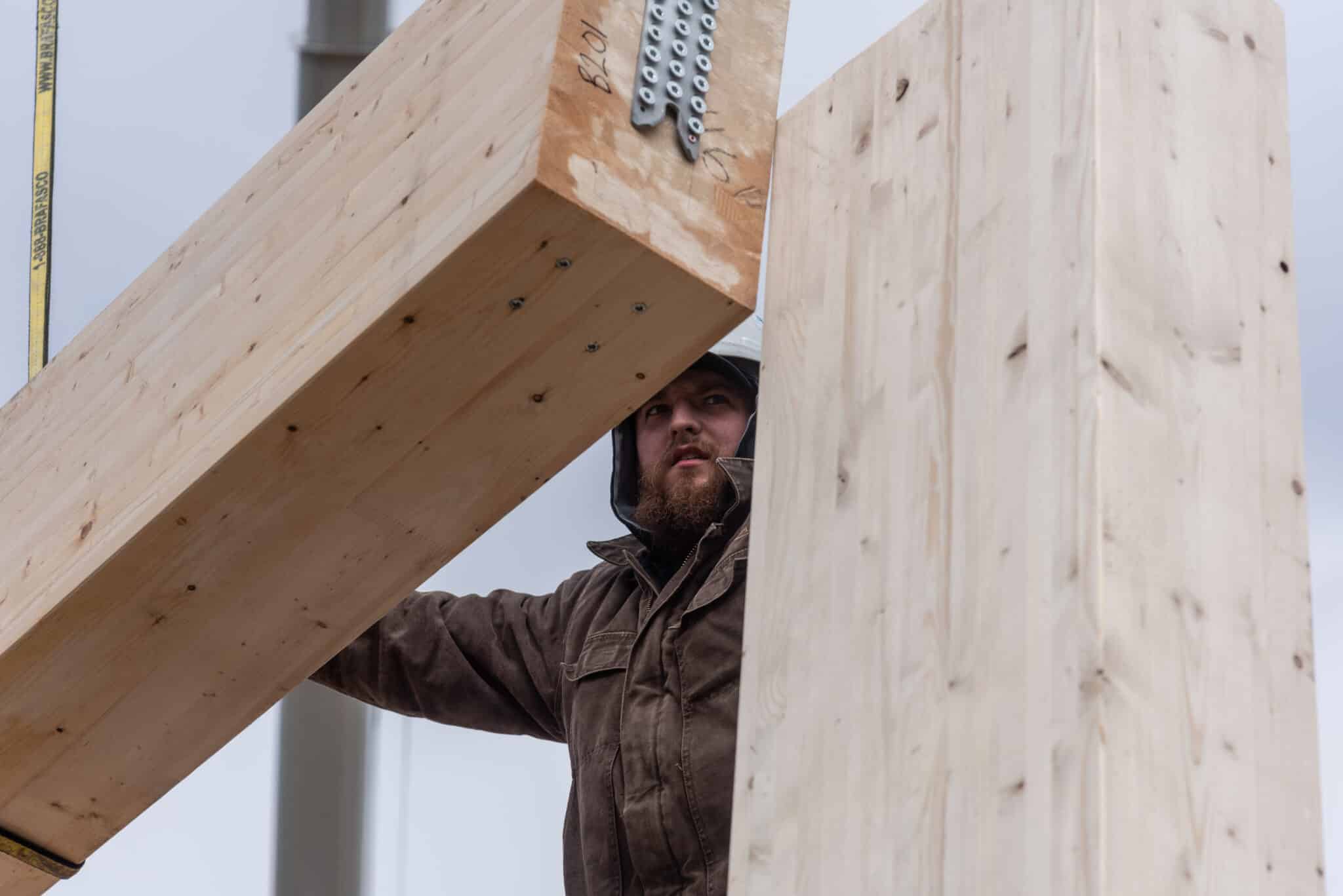
Welcome to the CWC Portal
Wood Design Tools & Calculators
The Canadian Wood Council (CWC) offers simple, easy-to-use, and free design tools to help architects, engineers, and builders work more efficiently with wood. From electronic design calculators to practical construction guides, our resources make wood design more accessible and straightforward.
CWC offers a number of free resources available to wood professionals as well as wood enthusiasts.
Exposed Mass Timber Calculator
Wind & Seismic Bracing Calculator
This interactive tool intends to aid in the design of the minimum braced wall panel length required for the houses based on seismic and wind forces.
Climate zone-appropriate insulated wall assembly solutions that are easily comparable with national and provincial energy efficiency prescriptive provisions.
Calculate load-carrying capacity for wood beams efficiently. Provides quick, code-compliant results for safe and reliable designs.
Dimension Calculator
Easily convert lumber dimensions for accurate planning. Ideal for ensuring precise cuts and minimizing waste.
Estimate lumber volume for your projects. Simplify material planning and cost estimation with accurate results.
Code CHEK
Ensure your designs meet safety standards. Verify compliance with the latest building codes for hassle-free projects.
FRR & STC Tool
Evaluate fire resistance and sound performance. Optimize designs to meet safety and acoustic standards easily.
Bolt Selection Table Viewer
Evaluate fire resistance and sound performance. Optimize designs to meet safety and acoustic standards easily.
Bolt Calculator
Performs design calculations for bolted connections in accordance with CSA O86:24 Clause 12.4.
The Canadian Wood Council’s Design Tools have been developed for information purposes only. Although all possible efforts have been made to ensure that the information on these tools is accurate, the CWC cannot under any circumstances guarantee the completeness, accuracy or exactness of the information. Reference should always be made to the appropriate Building Code and/or Standard. This tool should not be relied upon as a substitute for legal or design advice, and the user is responsible for how the tool is used or applied.
Explore Additional Tools
Expand your design capabilities with advanced tools tailored for timber construction. From calculators to performance modeling, these resources enhance your workflow for precise and efficient project execution.
Cecobois Online Tools
Climate zone-appropriate insulated wall assembly solutions that are easily comparable with national and provincial energy efficiency prescriptive provisions.
AWC Online Tools
Discover innovative tools designed to streamline your wood construction projects. Optimize design processes and explore solutions crafted for modern timber engineering.
Discover the WoodWorks® Software
Learn how the WoodWorks Software supports design and construction professionals with expert resources, tools, and free technical support for innovative wood building projects.
Explore Premium
Content and Resources
From best practices to innovative techniques, find everything you need to succeed in timber construction.
February 25, 2026 (Ottawa, ON) — The Canadian Wood Council (CWC) welcomes today’s launch of a national Call for Proposals by the Honourable Tim Hodgson, Minister of Energy and Natural Resources, under Natural Resources Canada’s forest sector transformation programs. Backed by a $500-million federal commitment, the funding is now open for applications from eligible businesses and organizations across Canada.
The call supports projects through four key programs:
- The Investments in Forest Industry Transformation (IFIT) program
- The Green Construction Through Wood (GCWood) program
- The Indigenous Forestry Initiative (IFI)
- The Global Forest Leadership Program (GloFor)
“This strategic investment comes at a pivotal time for Canada’s forest sector,” said Rick Jeffery, President and CEO of the Canadian Wood Council. “These programs can help accelerate modernization, support innovation, and expand the use of advanced wood solutions—strengthening our industry and opportunities within our domestic market while positioning Canada as a global leader in sustainable construction.”
Wood solutions are central to Canada’s built environment and economic future. Expanded use of wood in construction can support housing supply goals, reduce embodied carbon, and create new opportunities for growth and value-added manufacturing.
The Canadian Wood Council encourages members, partners, and wood products manufacturers to explore these funding opportunities to:
- innovate and diversify production
- strengthen domestic demand
- expand the use of wood in construction
- support Indigenous participation
- access emerging markets
About the Canadian Wood Council
The Canadian Wood Council (CWC) is Canada’s unifying voice for the wood products industry. As a national federation of associations, our members represent hundreds of manufacturers across the country. Our mission is to support our members by accelerating market demand for wood products and championing responsible leadership through excellence in codes, standards, and regulations. We also deliver technical support and knowledge transfer for the construction sector through our market leading WoodWorks program.
For media inquiries, please contact:
Sarah Hicks
Communications and Outreach Manager
Canadian Wood Council
shicks@cwc.ca | 1-705-796-3381
- Discover how tall mass timber is reshaping the future of affordable rental housing in this upcoming webinar from WoodWorks and StructureCraft. Scaling Affordable Rental Housing with Tall Mass Timber 📅 Thursday, March 5, 2026 | 🕐 10:00 AM PST | 1:00 PM EST As cities grapple with affordability and climate pressures, innovative projects are proving that mass timber can deliver practical, scalable solutions. This session explores Catalyst’s 18-storey CLT rental development in North Vancouver and the real-world strategies behind making tall mass timber projects viable and cost-competitive. Built for architects, engineers, developers, and municipal leaders, this webinar dives into key project insights — from structural grid constraints and moisture protection to prefabricated balcony systems and BIM-enabled coordination. You’ll also see how the team achieved near cost parity with concrete construction while integrating mixed-use programming and streamlining permitting. What you’ll gain: Practical approaches to applying tall mass timber hybrid systems in affordable and mixed-use housing Lessons learned from architectural, structural, and construction challenges unique to CLT buildings Proven strategies for permitting, procurement, coordination, and construction
- Unlock the secrets to designing custom steel connections for mass timber structures with our comprehensive presentation. Delve into the intricacies of custom connections versus predesigned alternatives, understanding the pros and cons inherent in each approach. Explore the critical role of load path determination and the array of options available to optimize structural performance. Navigate the complexities of eccentricity in connection design, gaining insights into how to effectively manage and mitigate its impact. Uncover the required checks and verifications essential for ensuring the structural integrity of your custom steel connections, with a step-by-step checklist that simplifies the process. We’ll address special considerations unique to mass timber applications, providing you with practical guidance on addressing challenges and optimizing connections for specific project needs. As we conclude, a comprehensive summary will tie together key takeaways, empowering you to confidently design custom steel connections that elevate the safety, efficiency, and resilience of mass timber structures. Join us for an enlightening journey through the intricacies of connection design, equipping you with the knowledge and tools needed to excel in the realm of mass timber construction.
Every issue of Wood Design & Building tells a different story about how wood is shaping contemporary construction. Some editions revolve around a clear theme such as our recent issue on strategic additions and adaptive reuse; others, like this one, reflect the diversity of challenges, innovations, and contexts that define wood construction today. What unites the features in this issue is not a single building type or region, but a shared commitment to thoughtful planning, ingenuity, and execution.
We begin in the mountains of British Columbia, where the Robson Cabin project pushes the limits of planning and coordination. Accessible only by helicopter, the remote alpine site demanded meticulous preparation, high levels of prefabrication, and an unwavering attention to detail. Alongside the technical complexity, the construction crew also contended with less predictable site conditions—including a persistent population of porcupines, whose curiosity added a memorable twist to an already remarkable build.
From there, we turn to one of the most sought-after—and often elusive—topics in the industry: cost. Reliable, project-specific costing data for mass timber buildings remains rare, and cost uncertainty can be a barrier to wider adoption of mass timber construction. This issue features an overview of a new mass timber business case study published by WoodWorks BC, which presents detailed cost, schedule, and design data from three projects. By comparing mass timber systems to conventional construction approaches across three building types, the study offers valuable insight into real-world construction costs, decision-making, and the strategies that can bring mass timber into cost parity.
Our final feature takes us to Trenton, Nova Scotia, for a virtual construction tour of the Pictou County Sports Heritage Hall of Fame, a community-focused project being realized through close collaboration between designers, builders, and trades. The one-storey building brings together panelized engineered wood walls, traditional light wood frame construction, and a central mass timber foyer, showcasing a deliberate “right material in the right place” approach. Built using offsite fabrication and carefully sequenced installation, the project demonstrates how coordination and precision can be leveraged to deliver a refined wood building that balances efficiency, constructability, and architectural expression.
Together, these stories offer a snapshot of a sector defined by creativity, technical rigor, and resilience—whether navigating rugged mountain terrain, unpacking the realities of construction costs, or reimagining how cultural buildings are delivered. We hope they inform, inspire, and perhaps even entertain.
- Presented by WoodWorks in partnership with DIALOG and Seagate Mass Timber. Join us for an exciting evening of networking and celebration at the Timber Afterparty following our WoodWorks @ BuildEx program, hosted in collaboration with industry leaders from DIALOG and Seagate. Why Attend? Network with Industry Experts: Connect with professionals, innovators, and enthusiasts from the wood industry. Learn and Share: Engage in insightful conversations about the latest trends, projects, and advancements in mass timber construction. Networking Opportunities: Build valuable connections and explore potential collaborations with peers. Enjoy a Relaxing Atmosphere: Join us for a drink and appetizers! Don’t miss out on this fantastic opportunity to mingle with like-minded professionals and gain new insights into the world of mass timber. Mark your calendars and join us for an evening of inspiration, knowledge-sharing, and community-building! Ticket includes appetizers and one (1) drink ticket.
- An introduction to mass timber as a design and construction material for architects, engineers, code officials, and contractors. A half-day seminar facilitated by the Canadian Society of Civil Engineering (CSCE), Saskatoon Section, in partnership with Woodworks. February 24th, 2026 The seminar will cover: Introduction to Woodworks and their available resources. Introduction to mass timber design – Fast & Epp structural engineers Mass timber installation and constructability – Beamcraft Fire and code considerations – Canadian Wood Council CLT manufacturing – Kalesnikoff Mass Timber Glulam fabrication – Western Archrib The seminar will include breakfast at 8:00am with the program starting at 8:30am. Lunch will be provided and we expect to conclude at 2:30pm. Location is the High Up Above A room at Staybridge Inn 1838 College Dr., Saskatoon, SK. Contact csce.saskatoon@gmail.com or David Wing at (306) 717-7651 with questions.
- Join WoodWorks, in collaboration with Scius Advisory, for a workshop exploring procurement challenges and opportunities for public projects. Designed for capital project managers and procurement professionals, this interactive workshop will explore practical strategies for integrating wood products and systems into public sector projects. Through facilitated round-table discussions, participants will examine how procurement decisions can enable the effective use of timber while managing risk, cost, and delivery expectations. The session welcomes municipal and provincial staff, school and park boards, and others involved in public procurement who are interested in using wood but encounter added complexity compared to conventional materials. Drawing on real-world case examples across a range of procurement models, the workshop will provide actionable insights and proven approaches to help inform future projects and procurement decisions. Pre-reading: Successful Delivery Methods for Procuring Mass Timber Buildings in Canada
- Join WoodWorks, in collaboration with Scius Advisory, for a workshop exploring procurement challenges and opportunities for public projects. Designed for capital project managers and procurement professionals, this interactive workshop will explore practical strategies for integrating wood products and systems into public sector projects. Through facilitated round-table discussions, participants will examine how procurement decisions can enable the effective use of timber while managing risk, cost, and delivery expectations. The session welcomes municipal and provincial staff, school and park boards, and others involved in public procurement who are interested in using wood but encounter added complexity compared to conventional materials. Drawing on real-world case examples across a range of procurement models, the workshop will provide actionable insights and proven approaches to help inform future projects and procurement decisions. Pre-reading: Successful Delivery Methods for Procuring Mass Timber Buildings in Canada
The ProTEKtor II® Technical Data Sheet provides detailed product and performance information for BarrierTEK’s ProTEKtor II® fire-protectant treatment used on wood frame and sheet components. The document is intended for designers, builders, specifiers, and code officials who require clear, concise technical data to support product evaluation and specification.
The TDS outlines key product characteristics, application parameters, and performance attributes for treated wood framing members and sheet goods, including compatibility considerations and relevant fire performance data. It serves as a practical reference for understanding how ProTEKtor II® is applied to enhance fire protection in both exposed and concealed wood-frame assemblies.
Developed as a technical reference, this data sheet supports accurate specification and informed use of ProTEKtor II®, helping project teams integrate fire-protectant-treated wood products into wood-frame construction with confidence and consistency.
The AtTEK® – Fire Protection for Attic Applications Technical Data Sheet provides detailed product and performance information for BarrierTEK’s AtTEK® fire-protectant treatment used in wood-frame attic assemblies. The document is intended for designers, builders, specifiers, and code officials requiring concise technical data to support product evaluation and specification.
The TDS outlines key product attributes, application parameters, and performance characteristics relevant to attic framing components, including treatment coverage, compatibility with wood products, and applicable fire performance considerations. It serves as a quick-reference resource for understanding how AtTEK® is used to enhance fire protection in concealed roof spaces.
Developed as a technical reference, this data sheet supports accurate specification and informed use of AtTEK® in attic applications, helping project teams integrate fire-protectant-treated wood into wood-frame buildings with clarity and confidence.
BarrierTEK’s Assurance with Insurance document outlines how the use of BarrierTEK fire-protectant-treated wood products can support risk management and insurance considerations in wood-frame construction. The resource is intended for building owners, developers, designers, and construction professionals seeking greater clarity on how fire performance measures may influence insurability and project risk profiles.
The document discusses the role of fire-protectant treatments in reducing fire risk, with a focus on concealed and exposed wood framing applications. It highlights how enhanced fire performance can align with insurer expectations and loss prevention strategies, helping project teams better understand the relationship between material selection, fire safety, and insurance outcomes.
Developed as an informational reference, Assurance with Insurance supports informed conversations between project stakeholders and insurance providers, offering insight into how proactive fire protection strategies can contribute to improved confidence and resilience in wood-frame buildings.
BarrierTEK’s ProTEKtor II® – High Performance Fire Protectant for Wood Frame & Sheet Components document provides technical guidance on the use of ProTEKtor II® fire-retardant treatment for improving fire performance in exposed and concealed wood-frame construction. The resource is intended for architects, engineers, builders, and code officials involved in projects where enhanced fire protection for wood framing and sheathing is required.
The document describes product properties, treatment processes, and performance characteristics of ProTEKtor II® when applied to wood frame members and sheet goods such as plywood and oriented strand board (OSB). It outlines how the treatment supports fire safety objectives by reducing flame spread and contributing to improved fire resistance across a range of wood-frame assemblies.
Developed as a practical technical reference, the ProTEKtor II® document supports informed specification and application of fire-protectant-treated wood products, helping project teams integrate enhanced fire performance into wood-frame buildings while addressing code and design considerations.
BarrierTEK’s AtTEK® – High Performance Fire Protectant for Wood Frame Attic Components document provides technical information on the use of AtTEK® fire-retardant treatment for enhancing fire performance in concealed wood framing applications. The resource is intended for designers, builders, and code officials involved in wood-frame construction where attic fire protection is a key consideration.
The document outlines product characteristics, treatment methods, and performance attributes of AtTEK® when applied to wood frame attic components, including framing members and assemblies located within concealed roof spaces. It describes how the treatment supports fire safety objectives by slowing flame spread and contributing to improved fire performance in vulnerable areas of wood-frame buildings.
Developed as a technical reference, the AtTEK® document supports informed decision-making during design, specification, and construction, helping project teams understand how fire-protectant-treated wood can be effectively incorporated into attic assemblies to meet project and code requirements.
The Nordic X-Lam Technical Guide is a comprehensive technical resource for architects, engineers, and construction professionals designing with cross-laminated timber (CLT) systems from Nordic Structures. The guide provides essential information to support the effective specification and integration of Nordic X-Lam panels in mass timber buildings.
The document details panel properties, structural performance, and typical applications, with guidance on sizing, spans, loading conditions, and connections. It also addresses key design considerations including fire performance, acoustics, vibration, and building code compliance, helping project teams evaluate system suitability across a range of project types.
Developed as a practical design reference, the Nordic X-Lam Technical Guide supports coordinated, efficient project delivery by providing a clear technical framework for incorporating CLT systems into contemporary wood construction.
The Nordic Structures LAM+™ Technical Guide is a comprehensive reference for designers, engineers, and builders working with LAM+™ mass timber floor and roof systems. Developed by Nordic Structures, the guide provides practical technical information to support the efficient and reliable specification of LAM+™ panels in a wide range of building types.
The document outlines system characteristics, structural performance considerations, and typical applications, with clear guidance on panel configuration, spans, loading, and integration with supporting structural systems. It also addresses key design considerations such as vibration performance, fire resistance, acoustics, and constructability to help project teams make informed decisions early in design.
Intended as a design aid, the LAM+™ Technical Guide supports collaboration between architects, structural engineers, and contractors, offering a consistent technical foundation for incorporating LAM+™ systems into mass timber projects.
This document provides guidance on common and effective procurement delivery methods for mass timber buildings in Canada, outlining how different approaches shape responsibility, decision-making, risk allocation, and communication across project teams. Emphasis is placed on the need for flexibility within procurement frameworks to accommodate the unique requirements of mass timber construction. Intended for owners, architects, engineers, contractors, and developers, the guide supports informed selection and implementation of procurement strategies that help address challenges related to supply, detailing, approvals, and delivery, enabling project teams to achieve coordinated, efficient project outcomes.

















