Bolts

Bolts are widely used in wood construction. They are able to resist moderately heavy loads with relatively few connectors. Bolts may be used in wood-to-wood, wood-to-steel and wood-to-concrete connection types. Some typical structural applications for bolts include: purlin to beam connections beam to column connections column to base connections truss connections timber arches post and beam construction pole-frame construction timber bridges marine structures Several types of bolts as shown in Figure 5.10 below, are used for wood construction with the hexagon head type being the most common. Countersunk heads are used where a flush surface is desired. Carriage bolts can be tightened by turning the nut without holding the bolt since the shoulders under the head grip the wood. Bolts are commonly available in imperial diameters of 1/4, 1/2, 5/8, 3/4, 7/8 and 1 inch. Bolts are installed in holes drilled slightly (1 to 2 mm) larger than the bolt diameter to prevent any splitting and stress development that could be caused by installation or subsequent wood shrinkage. Depending on the diameter, bolts are available in lengths from 75 mm (3″) up to 400 mm (16″) with other lengths available on special order. Bolts can be dipped or plated, at an additional cost, to provide resistance to corrosion. In exposed conditions and high moisture environments, corrosion should be resisted by using hot dip galvanized or stainless steel bolts, washers and nuts. Washers are commonly used with bolts to keep the bolt head or nut from crushing the wood member when tightening is taking place. Washers are not required with a steel side plate, as the bolt head or nut bears directly on the steel. Common types of washers are shown in Figure 5.11 below. Design information provided in CWC’s Wood Design Manual is based on bolts conforming to the requirements of ASTM A307 Standard Specification for Carbon Steel Bolts, Studs, and Threaded Rod 60 000 PSI Tensile Strength or Grade 2 bolts and dowels as specified under SAE J429 Mechanical and Material Requirements for Externally Threaded Fasteners. Download Figure 5.10 (and 5.11) as a PDF.
Framing Connectors

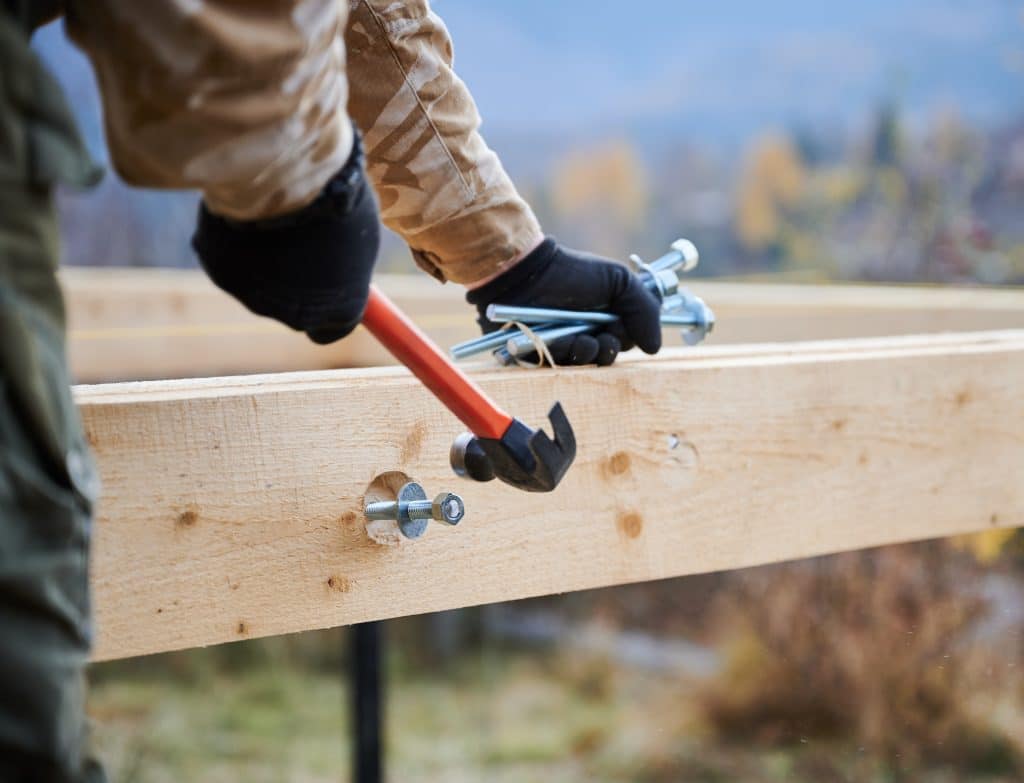
Framing connectors are proprietary products and include fastener types such as; framing anchors, framing angles, joist, purling and beam hangers, truss plates, post caps, post anchors, sill plate anchors, steel straps and nail-on steel plates. Framing connectors are often used for different reasons, such as; their ability to provide connections within prefabricated light-frame wood trusses, their ability to resist wind uplift and seismic loads, their ability to reduce the overall depth of a floor or roof assembly, or their ability to resist higher loads than traditional nailed connections. Examples of some common framing connectors are shown in Figure 5.6, below. Framing connectors are made of sheet metal and are manufactured with pre-punched holes to accept nails. Standard framing connectors are commonly manufactured using 20- or 18-gauge zinc coated sheet steel. Medium and heavy-duty framing connectors can be made from heavier zinc-coated steel, usually 12-gauge and 7-gauge, respectively. The load transfer capacity of framing connectors is related to the thickness of the sheet metal as well as the number of nails used to fasten the framing connector to the wood member. Framing connectors are suitable for most connection geometries that use dimensional lumber that is 38 mm (2″ nom.) and thicker lumber. In light-frame wood construction, framing connectors are commonly used in connections between joists and headers; rafters and plates or ridges; purlins and trusses; and studs and sill plates. Certain types of framing connectors, manufactured to fit larger wood members and carry higher loads, are also suitable for mass timber and post and beam construction. Manufacturers of the framing connectors will specify the type and number of fasteners, along with the installation procedures that are required in order to achieve the tabulated resistance(s) of the connection. The Canadian Construction Materials Centre (CCMC), Institute for Research in Construction (IRC), produce evaluation reports that document resistance values of framing connectors, which are derived from testing results. Figure 5.6 Framing Connectors For more information, refer to the following resources: Canadian Construction Material Centre, National Research Council of Canada Truss Plate Institute of Canada CSA S347 Method of Test for Evaluation of Truss Plates used in Lumber Joints ASTM D1761 Standard Test Methods for Mechanical Fasteners in Wood Canadian Wood Truss Association
Oriented Strand Board (OSB)
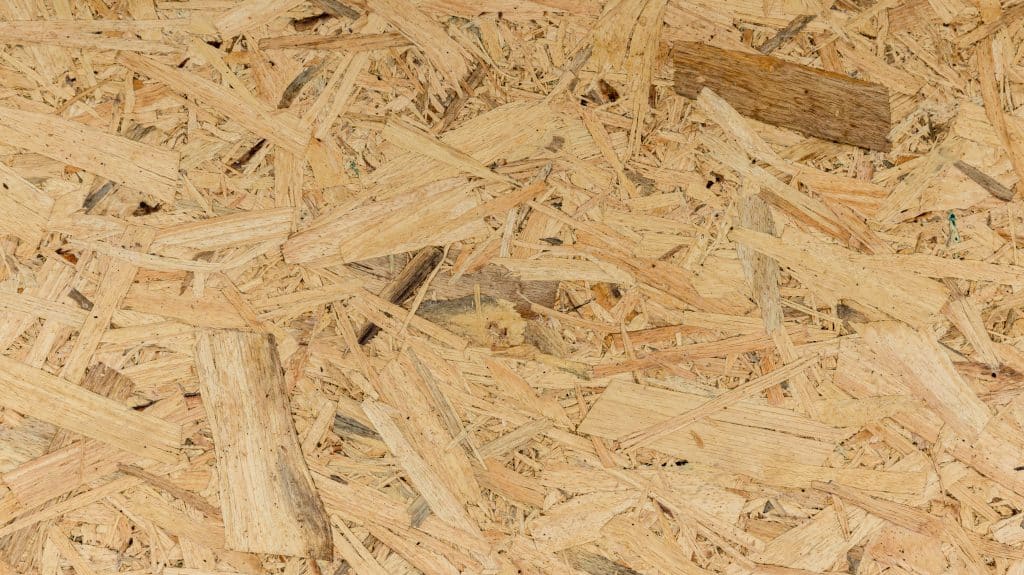

Oriented Strand Board (OSB) is a widely used, versatile structural wood panel. OSB makes efficient use of forest resources, by employing less valuable, fast-growing species. OSB is made from abundant, small diameter poplar and aspen trees to produce an economical structural panel. The manufacturing process can make use of crooked, knotty and deformed trees which would not otherwise have commercial value, thereby maximizing forest utilization. OSB has the ability to provide structural performance advantages, an important component of the building envelope and cost savings. OSB is a dimensionally stable wood-based panel that has the ability to resist delamination and warping. OSB can also resist racking and shape distortion when subjected to wind and seismic loadings. OSB panels are light in weight and easy to handle and install. OSB panels are primarily used in dry service conditions as roof, wall and floor sheathing, and act as key structural components for resisting lateral loads in diaphragms and shearwalls. OSB is also used as the web material for some types of prefabricated wood I-joists and the skin material for structural insulated panels. OSB can also be used in siding, soffit, floor underlayment and subfloor applications. Some specialty OSB products are made for siding and for concrete formwork, although OSB is not commonly treated using preservatives. OSB has many interleaved layers which provide the panel with good nail and screw holding properties. Fasteners can be driven as close as 6 mm (1/4 in) from the panel edge without risk of splitting or breaking out. OSB is a structural mat-formed panel product that is made from thin strands of aspen or poplar, sliced from small diameter roundwood logs or blocks, and bonded together with a waterproof phenolic adhesive that is cured under heat and pressure. OSB is also manufactured using the southern yellow pine species in the United States. Other species, such as birch, maple or sweetgum can also be used in limited quantities during manufacture. OSB is manufactured with the surface layer strands aligned in the long panel direction, while the inner layers have random or cross alignment. Similar to plywood, OSB is stronger along the long axis compared to the narrow axis. This random or cross orientation of the strands and wafers results in a structural engineered wood panel with consistent stiffness and strength properties, as well as dimensional stability. It is also possible to produce directionally-specific strength properties by adjusting the orientation of strand or wafer layers. The wafers or strands used in the manufacture of OSB are generally up to 150 mm (6 in) long in the grain direction, 25 mm (1 in) wide and less than 1 mm (1/32″) in thickness. In Canada, OSB panels are manufactured to meet the requirements of the CSA O325 standard. This standard sets performance ratings for specific end uses such as floor, roof and wall sheathing in light-frame wood construction. Sheathing conforming to CSA O325 is referenced in Part 9 of the National Building Code of Canada (NBC). In addition, design values for OSB construction sheathing are listed in CSA O86, allowing for engineering design of roof sheathing, wall sheathing and floor sheathing using OSB conforming to CSA O325. OSB panels are manufactured in both imperial and metric sizes, and are either square-edged or tongue-and-grooved on the long edges for panels 15 mm (19/32 in) and thicker. For more information on available sizes of OSB panel, refer to the document below. For more information on OSB, please refer to the following resources: APA – The Engineered Wood Association National Building Code of Canada CSA O86 Engineering design in wood CSA O325 Construction sheathing CSA O437 Standards on OSB and Waferboard PFS TECO Example specifications for oriented strand board (OSB) Oriented Strand Board (OSB) Grades Oriented Strand Board (OSB) Manufacture Oriented Strand Board (OSB) Quality Control Oriented Strand Board (OSB) Sizes Oriented Strand Board (OSB) Storage and Handling
Laminate Veneer Lumber
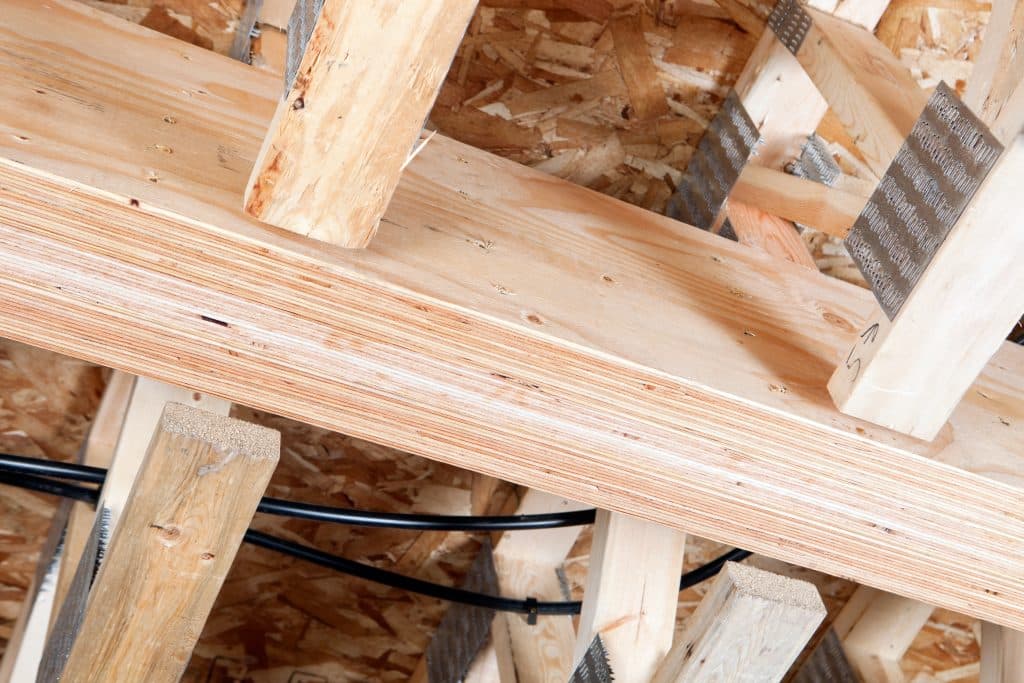

First used during World War II to make airplane propellers, laminated veneer lumber (LVL) has been available as a construction product since the mid-1970s. LVL is the most widely used structural composite lumber (SCL) product and provides attributes such as high strength, high stiffness and dimensional stability. The manufacturing process of LVL enables large members to be made from relatively small trees, providing efficient utilization of forest resources. LVL is commonly fabricated using wood species such as Douglas fir, Larch, Southern yellow pine and Poplar. LVL is used primarily as structural framing for residential and commercial construction. Common applications of LVL in construction include headers and beams, hip and valley rafters, scaffold planking, and the flange material for prefabricated wood I-joists. LVL can also been used in roadway sign posts and as truck bed decking. LVL is made of dried and graded wood veneer which is coated with a waterproof phenol-formaldehyde resin adhesive, assembled in an arranged pattern, and formed into billets by curing in a heated press. The LVL billet is then sawn to desired dimensions depending on the end use application. The grain of each layer of veneer runs in the same (long) direction with the result that LVL is able to be loaded on its short edge (strong axis) as a beam or on its wide face (weak axis) as a plank. This type of lamination is called parallel-lamination and produces a material with greater uniformity and predictability than engineered wood products fabricated using cross-lamination, such as plywood. LVL is a solid, highly predictable, uniform lumber product due to the fact that natural defects such as knots, slope of grain and splits have been dispersed throughout the material or have been removed altogether during the manufacturing process. The most common thickness of LVL is 45 mm (1-3/4 in), from which wider beams can be easily constructed by fastening multiple LVL plies together on site. LVL can also be manufactured in thicknesses from 19 mm (3/4 in) to 178 mm (7 in). Commonly used LVL beam depths are 241 mm (9-1/2 in), 302 mm (11-7/8 in), 356 mm (14 in), 406 mm (16 in), 476 mm (18-3/4 in) and 606 mm (23-7/8 in). Other widths and depths might also be available from specific manufacturers. LVL is available in lengths up to 24.4 m (80 ft), while more common lengths are 14.6 m (48 ft), 17 m (56 ft), 18.3 m (60 ft) and 20.1 m (66 ft). LVL can easily be cut to length at the jobsite. All special cutting, notching or drilling should be done in accordance with manufacturer’s recommendations. LVL is a wood-based product with similar fire performance to a comparably sized solid sawn lumber or glued-laminated beam. Manufacturer’s catalogues and evaluation reports are the primary sources of information for design, typical installation details and performance characteristics. LVL is mainly used as a structural element, most often in concealed spaces where appearance is not important. Finished or architectural grade appearance is available from some manufacturers, usually at an additional cost. However, when it is desired to use LVL in applications where appearance is important, common wood finishing techniques can be used to accent grain and to protect the wood surface. In finished appearance, LVL resembles plywood or lumber on the wide face. As with any other wood product, LVL should be protected from the weather during jobsite storage and after installation. Wrapping of the product for shipment to the job site is important in providing moisture protection. End and edge sealing of the product will enhance its resistance to moisture penetration. LVL is a proprietary product and therefore, the specific engineering properties and sizes are unique to each manufacturer. Thus, LVL does not have a common standard of production and common design values. Design values are derived from test results analysed in accordance with CSA O86 and ASTM D5456 and the design values are reviewed and approved by the Canadian Construction Materials Centre (CCMC). Products meeting the CCMC guidelines receive an Evaluation Number and Evaluation Report that includes the specified design strengths, which are subsequently listed in CCMC’s Registry of Product Evaluations. The manufacturer’s name or product identification and the stress grade is marked on the material at various intervals, but due to end cutting it may not be present on every piece. For further information, refer to the following resources: APA – The Engineered Wood Association Canadian Construction Materials Centre (CCMC), Institute for Research in Construction CSA O86 Engineering design in wood ASTM D5456 Standard Specification for Evaluation of Structural Composite Lumber Products
Laminated Strand Lumber
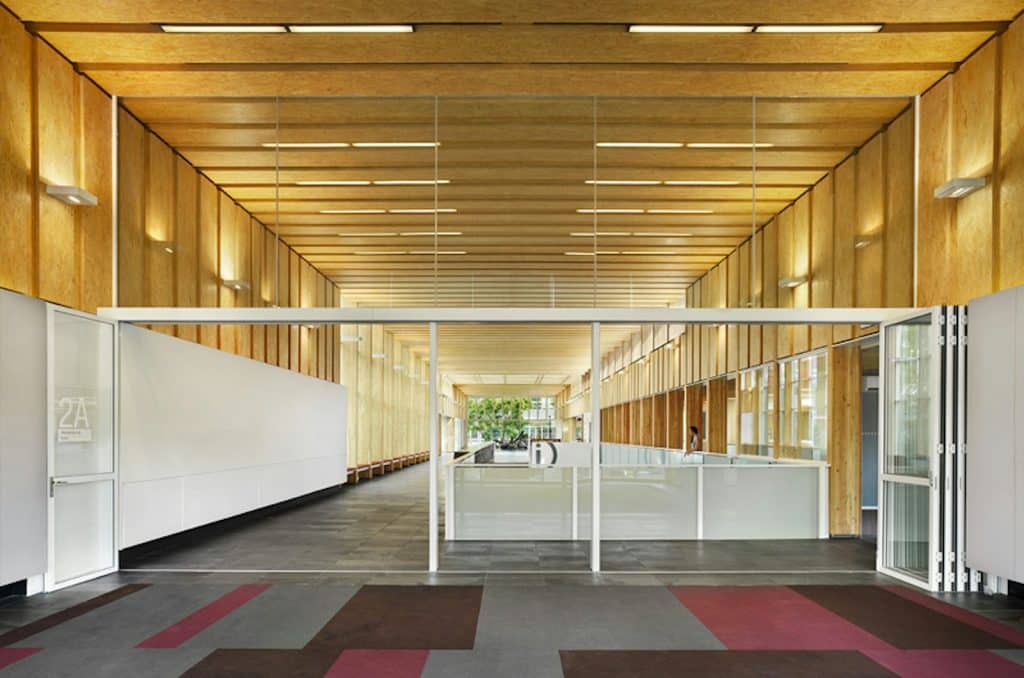

Laminated Strand Lumber (LSL) is one of the more recent structural composite lumber (SCL) products to come into widespread use. LSL provides attributes such as high strength, high stiffness and dimensional stability. The manufacturing process of LSL enables large members to be made from relatively small trees, providing efficient utilization of forest resources. LSL is commonly fabricated using fast growing wood species such as Aspen and Poplar. LSL is used primarily as structural framing for residential, commercial and industrial construction. Common applications of LSL in construction include headers and beams, tall wall studs, rim board, sill plates, millwork and window framing. LSL also offers good fastener-holding strength. Similar to parallel strand lumber (PSL) and oriented strand lumber (OSL), LSL is made from flaked wood strands that have a length-to-thickness ratio of approximately 150. Combined with an adhesive, the strands are oriented and formed into a large mat or billet and pressed. LSL resembles oriented strand board (OSB) in appearance as they are both fabricated from the similar wood species and contain flaked wood strands, however, unlike OSB, the strands in LSL are arranged parallel to the longitudinal axis of the member. LSL is a solid, highly predictable, uniform engineered wood product due to the fact that natural defects such as knots, slope of grain and splits have been dispersed throughout the material or have been removed altogether during the manufacturing process. Like other SCL products such as LVL and PSL, LSL offers predictable strength and stiffness properties and dimensional stability that minimize twist and shrinkage. All special cutting, notching or drilling should be done in accordance with manufacturer’s recommendations. Manufacturer’s catalogues and evaluation reports are the primary sources of information for design, typical installation details and performance characteristics. As with any other wood product, LSL should be protected from the weather during jobsite storage and after installation. Wrapping of the product for shipment to the job site is important in providing moisture protection. End and edge sealing of the product will enhance its resistance to moisture penetration. LSL is a proprietary product and therefore, the specific engineering properties and sizes are unique to each manufacturer. Thus, LSL does not have a common standard of production and common design values. Design values are derived from test results analysed in accordance with CSA O86 and ASTM D5456 and the design values are reviewed and approved by the Canadian Construction Materials Centre (CCMC). Products meeting the CCMC guidelines receive an Evaluation Number and Evaluation Report that includes the specified design strengths, which are subsequently listed in CCMC’s Registry of Product Evaluations. The manufacturer’s name or product identification and the stress grade is marked on the material at various intervals, but due to end cutting it may not be present on every piece. For further information, refer to the following resources: APA – The Engineered Wood Association Canadian Construction Materials Centre (CCMC), Institute for Research in Construction CSA O86 Engineering design in wood ASTM D5456 Standard Specification for Evaluation of Structural Composite Lumber Products
Cross-Laminated Timber (CLT)
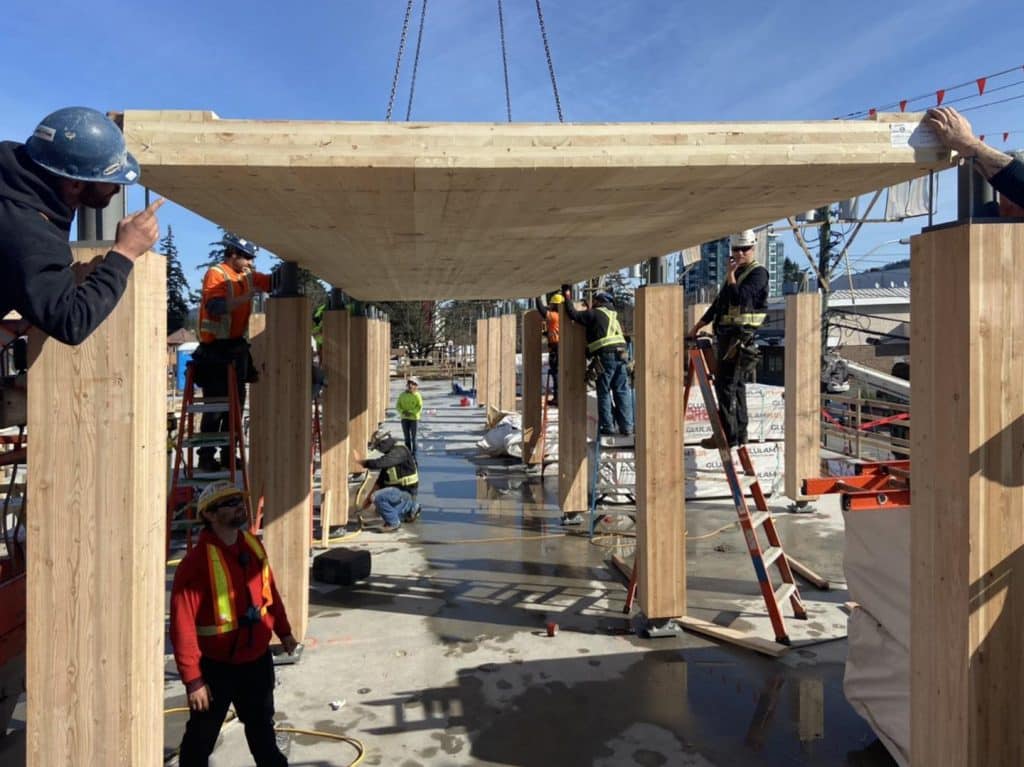

Cross-laminated timber (CLT) is a proprietary engineered wood product that is prefabricated using several layers of kiln-dried lumber, laid flat-wise, and glued together on their wide faces. Panels typically consist of three, five, seven or nine alternating layers of dimension lumber. The alternating directions of the CLT laminations provide it with high dimensional stability. CLT also has a high strength to weight ratio, along with exhibiting advantages for structural, fire, thermal and acoustic performance. Panel thicknesses usually range between 100 to 300 mm (4 to 12 in), but panels as thick as 500 mm (20 in) can be produced. Panel sizes range from 1.2 to 3 m (4 to 10 ft) in width and 5 to 19.5 m (16 to 64 ft) in length. The maximum panel size is limited by the size of the manufacturer’s press and transportation regulations. The design provisions for CLT in Canada apply to sawn lumber panels manufactured in accordance with the ANSI/APA PRG 320 standard. Typically, all the laminations in one direction are manufactured using the same grade and species of lumber. However, adjacent layers are permitted to be of different thickness and made of alternative grades or species. The moisture content of the lumber laminations at the time of CLT manufacturing is between 9 and 15%. There are five primary CLT stress grades; E1, E2, E3, V1 and V2. Stress grade E1 is the most readily available stress grade. The “E” designation indicates machine stress rated (MSR, or E-rated) lumber and the “V” designation indicates visually graded lumber. Stress grades E1, E2 and E3 consist of MSR lumber in all longitudinal layers and visually graded lumber in the transverse layers, while stress grades V1 and V2 consist of visually graded lumber in both longitudinal and transverse layers. Properties for custom CLT stress grades are also published by individual manufacturers. Similar to other proprietary structural wood products, CLT can be evaluated by the Canadian Construction Materials Centre (CCMC) in order to produce a product evaluation report. Unlike primary and custom CLT stress grades which are associated with structural capacity, appearance grades refer to the surface finish of CLT panels. Any stress grade can usually be produced in any surface finish targeted by the designer. Accommodations for reductions in strength and stiffness due to panel profiling or other face- or edge-finishes must be made. The Appendix of ANSI/APA PRG 320 provides examples of CLT appearance classifications. Structural adhesives used in bonding laminations must comply with CSA O112.10 and ASTM D7247 and are also evaluated for heat performance during exposure to fire. The different classes of structural adhesives that are typically used include: Emulsion polymer isocyanate (EPI); One-component polyurethane (PUR); Phenolic types such as phenol-resorcinol formaldehyde (PRF). Since pressure treatment with water-borne preservatives can negatively affect bond adhesion, CLT is not permitted to be treated with water-borne preservatives after gluing. For CLT treated with fire-retardant or other potentially strength-reducing chemicals, strength and stiffness is required to be based on documented test results. As part of the prefabrication process, CLT panels are cut to size, including door and window openings, with state-of-the art computer numerical controlled (CNC) routers, capable of making complex cuts with low tolerances. Prefabricated CLT elements arrive on site ready for immediate installation. CLT offers design flexibility and low environmental impacts for floor, roof and wall elements within innovative mid-rise and tall wood buildings. For further information on CLT, refer to the following resources: Kalesnikoff Nordic Structures APA – The Engineered Wood Association Canadian Construction Materials Centre (CCMC) Element5 ANSI/APA PRG 320 Standard for Performance-Rated Cross-Laminated Timber CSA O86 Engineering design in wood CSA O112.10 Evaluation of Adhesives for Structural Wood Products (Limited Moisture Exposure) ASTM D7247 Standard Test Method for Evaluating the Shear Strength of Adhesive Bonds in Laminated Wood Products at Elevated Temperatures
Glulam
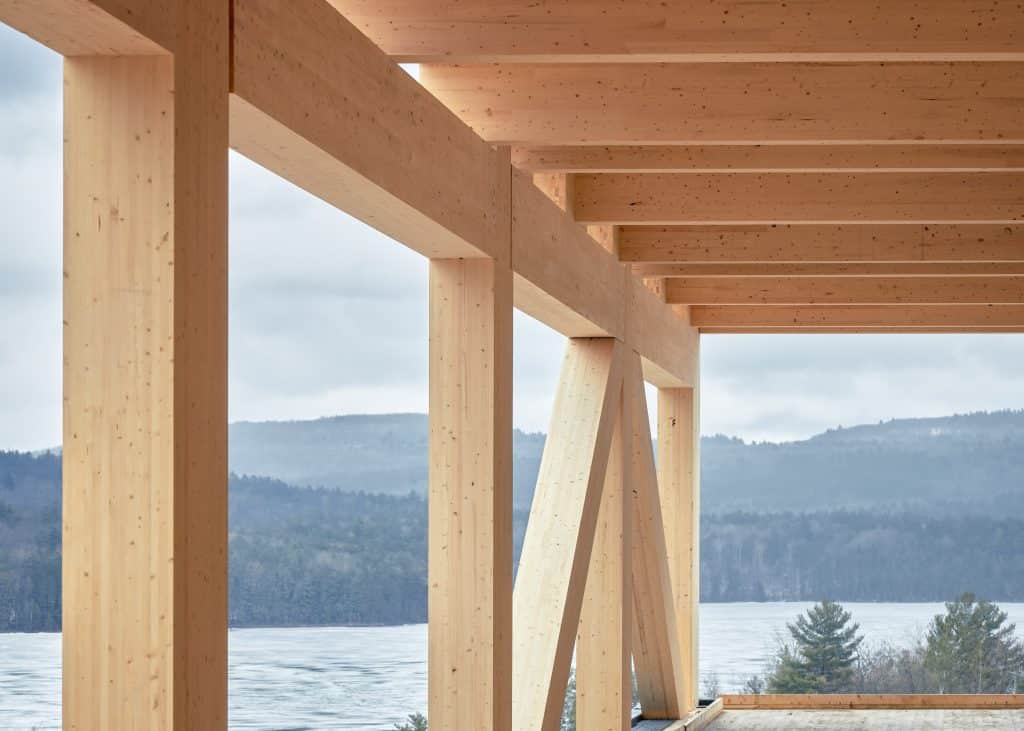

Glulam (glued-laminated timber) is an engineered structural wood product that consists of multiple individual layers of dimension lumber that are glued together under controlled conditions. All Canadian glulam is manufactured using waterproof adhesives for end jointing and for face bonding and is therefore suitable for both exterior and interior applications. Glulam has high structural capacity and is also an attractive architectural building material. Glulam is commonly used in post and beam, heavy timber and mass timber structures, as well as wood bridges. Glulam is a structural engineered wood product used for headers, beams, girders, purlins, columns, and heavy trusses. Glulam is also manufactured as curved members, which are typically loaded in combined bending and compression. It can also be shaped to create pitched tapered beams and a variety of load bearing arch and trusses configurations. Glulam is often employed where the structural members are left exposed as an architectural feature. Available sizes of glulam Standard sizes have been developed for Canadian glued-laminated timber to allow optimum utilization of lumber which are multiples of the dimensions of the lamstock used for glulam manufacture. Suitable for most applications, standard sizes offer the designer economy and fast delivery. Other non-standard dimensions may be specially ordered at additional cost because of the extra trimming required to produce non-standard sizes. The standard widths and depths of glulam are shown in Table 6.7, below. The depth of glulam is a function of the number of laminations multiplied by the lamination thickness. For economy, 38 mm laminations are used wherever possible, and 19 mm laminations are used where greater degrees of curvature are required. Standard widths of glulam Standard finished widths of glulam members and common widths of the laminating stock they are made from are given in Table 4 below. Single widths of stock are used for the complete width dimension for members less than 275 mm (10-7/8″) wide. However, members wider than 175 mm (6-7/8″) may consist of two boards laid side by side. All members wider than 275 mm (10-7/8″) are made from two pieces of lumber placed side by side, with edge joints staggered within the depth of the member. Members wider than 365 mm (14-1/4″) are manufactured in 50 mm (2″) width increments, but will be more expensive than standard widths. Manufacturers should be consulted for advice. Initial width of glulam stock Finished width of glulam stock mm. in. mm. in. 89 3-1/2 80 3 140 5-1/2 130 5 184 7-1/4 175 6-7/8 235 (or 89 + 140) 9-1/4 (or 3-1/2 + 5-1/2) 225 (or 215) 8-7/8 (or 8-1/2) 286 (or 89 + 184) 11-1/4 (or 3-1/2 + 7-1/4) 275 (or 265) 10-7/8 (or 10-1/4) 140 + 184 5-1/2 + 7-1/4 315 12-1/4 140 + 235 5-1/2 + 9-1/4 365 14-1/4 Notes: Members wider than 365 mm (14-1/4″) are available in 50 mm (2″) increments but require a special order. Members wider than 175 mm (6-7/8″) may consist of two boards laid side by side with logitudinal joints staggered in adjacent laminations. Standard depths of glulam Standard depths for glulam members range from 114 mm (4-1/2″) to 2128 mm (7′) or more in increments of 38 mm (1-1/2″) and l9 mm (3/4″). A member made from 38 mm (1-1/2″) laminations costs significantly less than an equivalent member made from l9 mm (3/4″) laminations. However, the l9 mm (3/4″) laminations allow for a greater amount of curvature than do the 38 mm (1-1/2″) laminations. Width in. Depth range mm in. 80 3 114 to 570 4-1/2 to 22-1/2 130 5 152 to 950 6 to 37-1/2 175 6-7/8 190 to 1254 7-1/2 to 49-1/2 215 8-1/2 266 to 1596 10-1/2 to 62-3/4 265 10-1/4 342 to 1976 13-1/2 to 77-3/4 315 12-1/4 380 to 2128 15 to 83-3/4 365 14-1/4 380 to 2128 15 to 83-3/4 Note: 1. Intermediate depths are multiples of the lamination thickness, which is 38 mm (1-1/2″ nom.) except for some curved members that require 19 mm (3/4″ nom.) laminations. Laminating stock may be end jointed into lengths of up to 40 m (130′) but the practical limitation may depend on transportation clearance restrictions. Therefore, shipping restrictions for a given region should be determined before specifying length, width or shipping height. Glulam appearance grades In specifying Canadian glulam products, it is necessary to indicate both the stress grade and the appearance grade required. The appearance of glulam is determined by the degree of finish work done after laminating and not by the appearance of the individual lamination pieces. Glulam is available in the following appearance grades: Industrial Commercial Quality The appearance grade defines the amount of patching and finishing work done to the exposed surfaces after laminating (Table 6.8) and has no strength implications. Quality grade provides the greatest degree of finishing and is intended for applications where appearance is important. Industrial grade has the least amount of finishing. Grade Description Industrial Grade Intended for use where appearance is not a primary concern such as in industrial buildings; laminating stock may contain natural characteristics allowed for specified stress grade; sides planed to specified dimensions but occasional misses and rough spots allowed; may have broken knots, knot holes, torn grain, checks, wane and other irregularities on surface. Commercial Grade Intended for painted or flat-gloss varnished surfaces; laminating stock may contain natural characteristics allowed for specified stress grade; sides planed to specified dimensions and all squeezed-out glue removed from surface; knot holes, loose knots, voids, wane or pitch pockets are not replaced by wood inserts or filler on exposed surface. Quality Grade Intended for high-gloss transparent or polished surfaces, displays natural beauty of wood for best aesthetic appeal; laminating stock may contain natural characteristics allowed for specified stress grade; sides planed to specified dimensions and all squeezed-out glue removed from surface; may have tight knots, firm heart stain and medium sap stain on sides; slightly broken or split knots, slivers, torn grain or checks on surface filled; loose knots, knot holes, wane and pitch pockets removed and replaced with non-shrinking
Panel Products

By using roundwood that is often not be suitable for lumber production, wood-based panels make efficient use of the forest resource by providing engineered wood products with defined strength and stiffness properties. Wood-based structural panels such as plywood and oriented strand board (OSB) are widely used in residential and commercial construction. Wood-based panels are often overlaid on joists or light frame trusses and used as structural sheathing for floor, roofs and wall assemblies. These products provide rigidity to the supporting main structural members in addition to their function as a component of the building envelope. In addition, they are often an integral component of the lateral force resisting system of a wood building. In order to qualify for a particular end use, such as structural sheathing, flooring or exterior siding, wood-based panels must meet performance criteria related to three aspects: structural performance, physical properties and bond performance. For more information on performance rating and potential end uses of wood-based panel products, refer to APA – The Engineered Wood Association.
Oriented Strand Lumber

Oriented Strand Lumber (OSL) Oriented Strand Lumber (OSL) provides attributes such as high strength, high stiffness and dimensional stability. The manufacturing process of OSL enables large members to be made from relatively small trees, providing efficient utilization of forest resources. OSL is used primarily as structural framing for residential, commercial and industrial construction. Common applications of OSL in construction include headers and beams, tall wall studs, rim board, sill plates, millwork and window framing. OSL also offers good fastener-holding strength. Similar to laminated strand lumber (LSL), OSL is made from flaked wood strands that have a length-to-thickness ratio of approximately 75. The wood strands used in OSL are shorter than those in LSL. Combined with an adhesive, the strands are oriented and formed into a large mat or billet and pressed. OSL resembles oriented strand board (OSB) in appearance as they are both fabricated from the similar wood species and contain flaked wood strands, however, unlike OSB, the strands in OSL are arranged parallel to the longitudinal axis of the member. OSL is a solid, highly predictable, uniform engineered wood product due to the fact that natural defects such as knots, slope of grain and splits have been dispersed throughout the material or have been removed altogether during the manufacturing process. Like other SCL products such as LVL and PSL, OSL offers predictable strength and stiffness properties and dimensional stability that minimize twist and shrinkage. All special cutting, notching or drilling should be done in accordance with manufacturer’s recommendations. Manufacturer’s catalogues and evaluation reports are the primary sources of information for design, typical installation details and performance characteristics. As with any other wood product, OSL should be protected from the weather during jobsite storage and after installation. Wrapping of the product for shipment to the job site is important in providing moisture protection. End and edge sealing of the product will enhance its resistance to moisture penetration. OSL is a proprietary product and therefore, the specific engineering properties and sizes are unique to each manufacturer. Thus, OSL does not have a common standard of production and common design values. Design values are derived from test results analysed in accordance with CSA O86 and ASTM D5456 and the design values are reviewed and approved by the Canadian Construction Materials Centre (CCMC). Products meeting the CCMC guidelines receive an Evaluation Number and Evaluation Report that includes the specified design strengths, which are subsequently listed in CCMC’s Registry of Product Evaluations. The manufacturer’s name or product identification and the stress grade is marked on the material at various intervals, but due to end cutting it may not be present on every piece. For further information, refer to the following resources: APA – The Engineered Wood Association Canadian Construction Materials Centre (CCMC), Institute for Research in Construction CSA O86 Engineering design in wood ASTM D5456 Standard Specification for Evaluation of Structural Composite Lumber Products
Parallel Strand Lumber
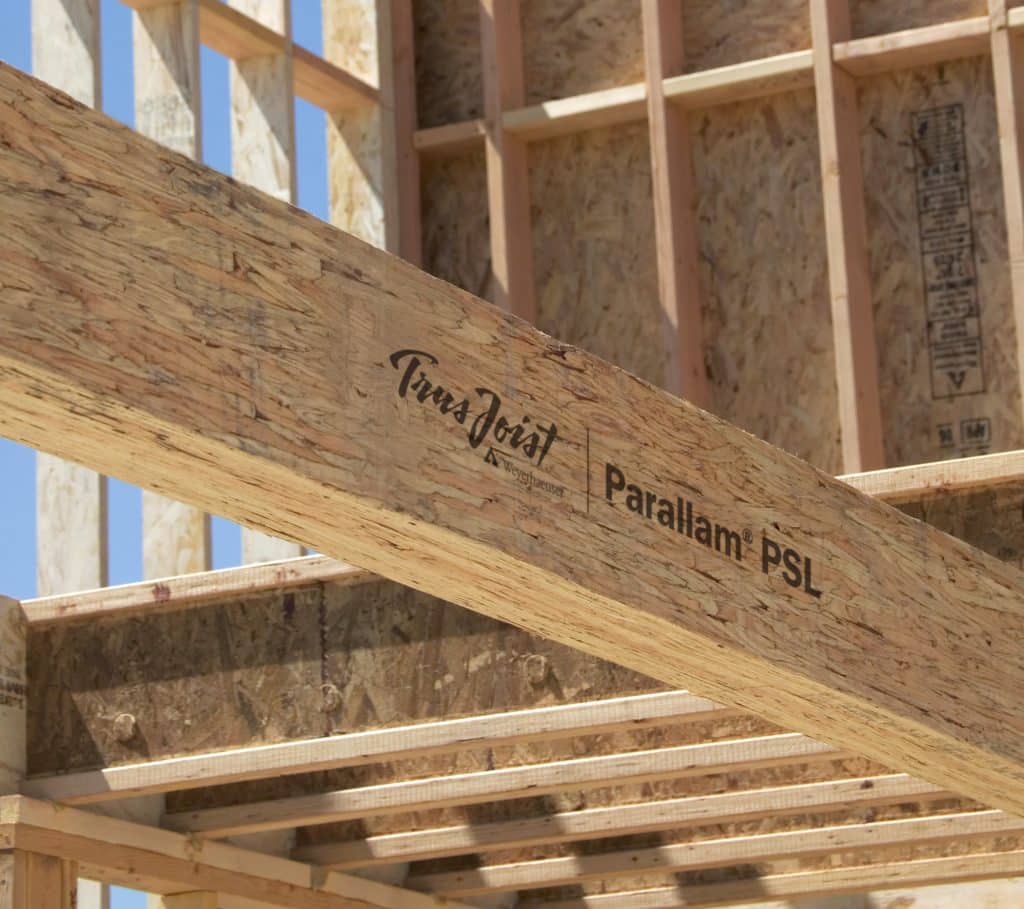

Parallel Strand Lumber (PSL) Parallel Strand Lumber (PSL) provides attributes such as high strength, high stiffness and dimensional stability. The manufacturing process of OSL enables large members to be made from relatively small trees, providing efficient utilization of forest resources. In Canada, PSL is fabricated using Douglas fir. PSL is employed primarily as structural framing for residential, commercial and industrial construction. Common applications of PSL in construction include headers, beams and lintels in light-frame construction and beams and columns in post and beam construction. PSL is an attractive structural material which is suited to applications where finished appearance is important. Similar to laminated strand lumber (LSL) and oriented strand lumber (OSL), PSL is made from flaked wood strands that are arranged parallel to the longitudinal axis of the member and have a length-to-thickness ratio of approximately 300. The wood strands used in PSL are longer than those used to manufacture LSL and OSL. Combined with an exterior waterproof phenol-formaldehyde adhesive, the strands are oriented and formed into a large billet, then pressed together and cured using microwave radiation. PSL beams are available in thicknesses of 68 mm (2-11/16 in), 89 mm (3-1/2 in), 133 mm (5-1/4 in), and 178 mm (7 in) and a maximum depth of 457 mm (18 in). PSL columns are available in square or rectangular dimensions of 89 mm (3-1/2 in), 133 mm (5-1/4 in), and 178 mm (7 in). The smaller thicknesses can be used individually as single plies or can be combined for multi-ply applications. PSL can be made in long lengths but it is usually limited to 20 m (66 ft) by transportation constraints. PSL is a solid, highly predictable, uniform engineered wood product due to the fact that natural defects such as knots, slope of grain and splits have been dispersed throughout the material or have been removed altogether during the manufacturing process. Like the other SCL products (LVL, LSL and OSL), PSL offers predictable strength and stiffness properties and dimensional stability. Manufactured at a moisture content of 11 percent, PSL is less prone to shrinking, warping , cupping, bowing and splitting. All special cutting, notching or drilling should be done in accordance with manufacturer’s recommendations. Manufacturer’s catalogues and evaluation reports are the primary sources of information for design, typical installation details and performance characteristics. PSL exhibits a rich texture and retains numerous dark glue lines. PSL can be machined, stained, and finished using the techniques applicable to sawn lumber. PSL members readily accept stain to enhance the warmth and texture of the wood. All PSL is sanded at the end of the production process to ensure precise dimensions and to provide a high quality surface for appearance. As with any other wood product, PSL should be protected from the weather during jobsite storage and after installation. Wrapping of the product for shipment to the job site is important in providing moisture protection. End and edge sealing of the product will enhance its resistance to moisture penetration. PSL readily accepts preservative treatment and it is possible to obtain a high degree of preservative penetration. Treated PSL can be specified in high humidity exposures. PSL is a proprietary product and therefore, the specific engineering properties and sizes are unique to each manufacturer. Thus, PSL does not have a common standard of production and common design values. Design values are derived from test results analysed in accordance with CSA O86 and ASTM D5456 and the design values are reviewed and approved by the Canadian Construction Materials Centre (CCMC). Products meeting the CCMC guidelines receive an Evaluation Number and Evaluation Report that includes the specified design strengths, which are subsequently listed in CCMC’s Registry of Product Evaluations. The manufacturer’s name or product identification and the stress grade is marked on the material at various intervals, but due to end cutting it may not be present on every piece. The Canadian Construction Materials Centre (CCMC) has accepted PSL for use as heavy timber construction, as described under the provisions within Part 3 of the National Building Code of Canada. For further information, refer to the following resources: APA – The Engineered Wood Association Canadian Construction Materials Centre (CCMC), Institute for Research in Construction CSA O86 Engineering design in wood ASTM D5456 Standard Specification for Evaluation of Structural Composite Lumber Products
Solid-Sawn Heavy Timber

Solid-sawn heavy timber members are predominantly employed as the main structural elements in post and beam construction. The term ‘heavy timber’ is used to describe solid sawn lumber which is 140 mm (5-1/2 in) or more in its smallest cross-sectional dimension. Large dimension timbers offer increased fire resistance compared to dimensional lumber and can be used to meet the heavy timber construction requirements outlined in the Part 3 of the National Building Code of Canada. Sawn timbers are produced in accordance with CSA O141 Canadian Standard Lumber and graded in accordance with the NLGA Standard Grading Rules for Canadian Lumber. There are two categories of timbers; rectangular “Beams and Stringers” and square “Posts and Timbers”. Beams and Stringers, whose larger dimension exceeds its smaller dimension by more than 51 mm (2 in), are typically used as bending members, whereas, Posts and Timbers, whose larger dimension exceeds its smaller dimension by 51 mm (2 in) or less, are typically used as columns. Sawn timbers range in size from 140 to 394 mm (5-1/2 to 15-1/2 in). The most common sizes range from 140 x 140 mm (5-1/2 x 5-1/2 in) to 292 x 495 mm (11-1/2 x 19-1/2 in) in lengths of 5 to 9 m (16 to 30 ft). Sizes up to 394 x 394 mm (15-1/2 x 15-1/2 in) are generally available from Western Canada in the Douglas Fir-Larch and Hem-Fir species combinations. Timbers from the Spruce-Pine-Fir (S-P-F) and Northern species combinations are only available in smaller sizes. Timbers may be obtained in lengths up to 9.1 m (30 ft), but the availability of large size and long length timbers should always be confirmed with suppliers prior to specifying. A table of available timber sizes is shown below. Both categories of timbers, Beams and Stringers, and Posts and Timbers, contain three stress grades: Select Structural, No.1, and No.2, and two non-stress grades (Standard and Utility). The stress grades are assigned design values for use as structural members. Non-stress grades have not been assigned design values. No.1 or No.2 are the most common grades specified for structural purposes. No.1 may contain varying amounts of Select Structural, depending on the manufacturer. Unlike Canadian dimension lumber, there is a difference between design values for No.1 and No.2 grades for timbers. Select Structural is specified when the highest quality appearance and strength are desired. The Standard and Utility grades have not been assigned design values. Timbers of these grades are permitted for use in specific applications of building codes where high strength is not important, such as blocking or short bracing. Cross cutting can affect the grade of timber in the Beams and Stringers category because the allowable size of knot varies along the length of the piece (a larger knot is allowed near the ends than in the middle). Timbers must be regraded if cross cut. Timbers are generally not grade marked (grade stamped) and a mill certificate can be obtained to certify the grade. The large size of timbers makes kiln drying impractical due to the drying stresses which would result from differential moisture contents between the interior and exterior of the timber. For this reason, timbers are usually dressed green (moisture content above 19 percent), and the moisture content of timber upon delivery will depend on the amount of air drying which has taken place. Like dimension lumber, timber begins to shrink when its moisture content falls below about 28 percent. Timbers exposed to the outdoors usually shrink from 1.8 to 2.6 percent in width and thickness, depending on the species. Timbers used indoors, where the air is often drier, experience greater shrinkage, in the range of 2.4 to 3.0 percent in width and thickness. Length change in either case is negligible. Allowances for anticipated shrinkage should be made in the design and construction. Shrinkage should also be considered when designing connections. Minor checks on the surface of a timber are common in both wet and dry service conditions. Consideration has been made for these surface checks in the establishment of specified design strengths. Checks in columns are not of structural importance unless the check develops into a through split that will divide the column. For further information, refer to the following resources: Timber Framers Guild International Log Builders’ Association BC Log & Timber Building Industry Association
Plank Decking

Plank decking may be used to span farther and carry greater loads than panel products such as plywood and oriented strand board (OSB). Plank decking is often used where the appearance of the decking is desired as an architectural feature or where the fire performance must meet the heavy timber construction requirements outlined in Part 3 of the National Building Code of Canada. Plank decking is usually used in mass timber or post and beam structures and is laid with the flat or wide face over supports to provide a structural deck for floors and roofs. Plank decking can be used in either wet or dry service conditions and can be treated with preservatives, dependent on the wood species. Nails and deck spikes are used to fasten adjacent pieces of plank decking to one another and are also used to fasten the deck to its supports. Decking is generally available in the following species: Douglas fir (D.Fir-L species combination) Pacific coast hemlock (Hem-Fir species combination) Various species of spruce, pine and fir (S-P-F species combination) Western red cedar (Northern species combination) In order to product plank decking, sawn lumber is milled into a tongue and groove profile with special surface machining, such as a V-joint. Plank decking is normally produced in three thicknesses: 38 mm (1-1/2 in), 64 mm (2-1/2 in) and 89 mm (3-1/2 in). The 38 mm (1-1/2 in) decking has a single tongue and groove while the thicker sizes have a double tongue and groove. Thicknesses greater than 38 mm (1-1/2 in) also have 6 mm (1/4 in) diameter holes at 760 mm (2.5 ft) spacing so that each piece may be nailed to the adjacent one with deck spikes. The standard sizes and profiles are shown below. Plank decking is most readily available in random lengths of 1.8 to 6.1 m (6 to 20 ft). Decking can be ordered in specific lengths, but limited availability and extra costs should be expected. A typical specification for random lengths could require that at least 90 percent of the plank decking be 3.0 m (10 ft) and longer, and at least 40 percent be 4.9 m (16 ft) and longer. Plank decking is available in two grades: Select grade (Sel) Commercial grade (Com) Select grade has a higher quality appearance and is also stronger and stiffer than commercial grade. Plank decking is required to be manufactured in accordance with CSA O141 and graded under the NLGA Standard Grading Rules for Canadian Lumber. Since plank decking is not grade stamped like dimensional lumber, verification of the grade should be obtained in writing from the supplier or a qualified grading agency should be retained to check the supplied material. To minimize shrinkage and warping, plank decking consists of sawn lumber members that are dried to a moisture content of 19 percent or less at the time of surfacing (S-Dry). The use of green decking can result in the loosening of the tongue and groove joint over time and a reduction in structural and serviceability performance. Individual planks can span simply between supports, but are generally random lengths spanning several supports for economy and to take advantage of increased stiffness. There are three methods of installing plank decking: controlled random, simple span and two span continuous. A general design rule for controlled random plank decking is that spans should not be more than 600 mm (2 ft) longer than the length which 40 percent of the decking shipment exceeds. Both the latter methods of installation require planks of predetermined length and a consequently there could be an associated cost premium. Profiles and Sizes of Plank Decking