Standard Connections, Issue 1: Gravity – Solutions Paper

Connection design variability is often considered to be a significant cost driver for mass timber projects, yet designers often lack clear guidance on what standard solutions could look like. The purpose of this document is to provide the construction industry with standardized detailing practices that cover a wide range of connections commonly found in mass timber buildings in Canada. These details can be adapted across multiple projects with various design teams and suppliers. The focus is on providing high-capacity, simple installation, and overall cost-effectiveness for timber connections. Six details are presented based on typical beam, column, and wall connections. This document also outlines the design focus areas that were prioritized during detail development. Lastly, a checklist is provided for detailers to ensure that all priorities are considered. Companion 3D versions of these details can downloaded here.
2025 Catherine Lalonde Memorial Scholarships Recognize Students Advancing the Next Generation of Wood Solutions

Ottawa, ON, December 16, 2025 – The Canadian Wood Council (CWC) is pleased to announce three recipients of the 2025 Catherine Lalonde Memorial Scholarship: Houman Ganjali (University of Northern British Columbia), Kalkidan Tesfaye Shewandagn (McGill University), and Henri Monette (University of Toronto). These exceptional graduate students were selected for their academic excellence and their cutting-edge research advancing innovation in structural wood products and wood-based construction systems. Established twenty years ago, the memorial scholarships honour the legacy of Catherine Lalonde, whose leadership as a professional engineer and president of the CWC helped shape the trajectory of wood design and construction in Canada. Each year, the awards recognize graduate students whose research reflects the same commitment to scientific excellence, industry impact, and passion for wood that Catherine championed throughout her career. This year, the Canadian Wood Council received 51 submissions, a record for the program. The submissions reflected a high level of academic discipline and a strong orientation toward industry-relevant challenges, an indication of both the vitality of the research community and the growing importance of wood-based solutions in the built environment. Houman Ganjali Houman is a 5th year PhD candidate in Engineering at the University of Northern British Columbia. His research investigates the structural performance of point-supported cross-laminated timber (CLT) floors, focusing on the rolling-shear strength of CLT panels and the punching-shear capacity of point-supported systems. His work also examines improved connection strategies along the minor strength axis, reinforcement approaches for point supports, and the creep and vibration behaviour of point-supported floors. Houman’s research culminated in the development of a design proposal for the resistance of point-supported CLT floors, which will be presented to the CSA O86 Technical Committee for potential inclusion in future editions of the standard. Kalkidan Tesfaye Shewandagn Kalkidan is a 2nd year PhD student in Civil Engineering at McGill University. Her research focuses on the seismic design and performance assessment of wood-frame buildings constructed over podium structures. By integrating experimental testing, nonlinear modelling (OpenSeesPy), and performance-based assessment, her work quantifies the interaction between wood-frame systems and podiums. The resulting guidelines aim to support broader adoption of wood in multi-storey and hybrid buildings across Canada. Henri Monette Henri is a 4th year PhD candidate in Civil and Mineral Engineering at the University of Toronto. His research explores the development of a high-resistance connector for mass timber structures—an innovative system designed to optimize fibre use by mobilizing the full sectional resistance of connected timber members. By addressing the strength and resilience limitations of current connection technologies, Henri’s work supports mass timber’s ability to compete with and displace traditional materials such as steel and concrete. “The large number of submissions we received this year signals the impressive depth of wood-focused research underway across Canada,” said Blériot Feujofack, Manager of Wood Education at the Canadian Wood Council. “This year’s scholarship recipients stand as strong examples of the academic excellence demonstrated throughout the applicant pool, distinguished by their clear methodological strength and practical relevance. Their findings hold meaningful value for practitioners, code developers, and industry partners, and will contribute to the continued advancement of wood construction in Canada.” About the Canadian Wood Council The Canadian Wood Council (CWC) is Canada’s unifying voice for the wood products industry. As a national federation of associations, its members represent hundreds of manufacturers across the country. CWC supports its members by accelerating market demand for wood products and championing responsible leadership through excellence in codes, standards, and regulations. CWC also delivers technical support and knowledge transfer for the construction sector through its market leading WoodWorks program.
Canadian Wood Council Advances Wood Innovation and Education

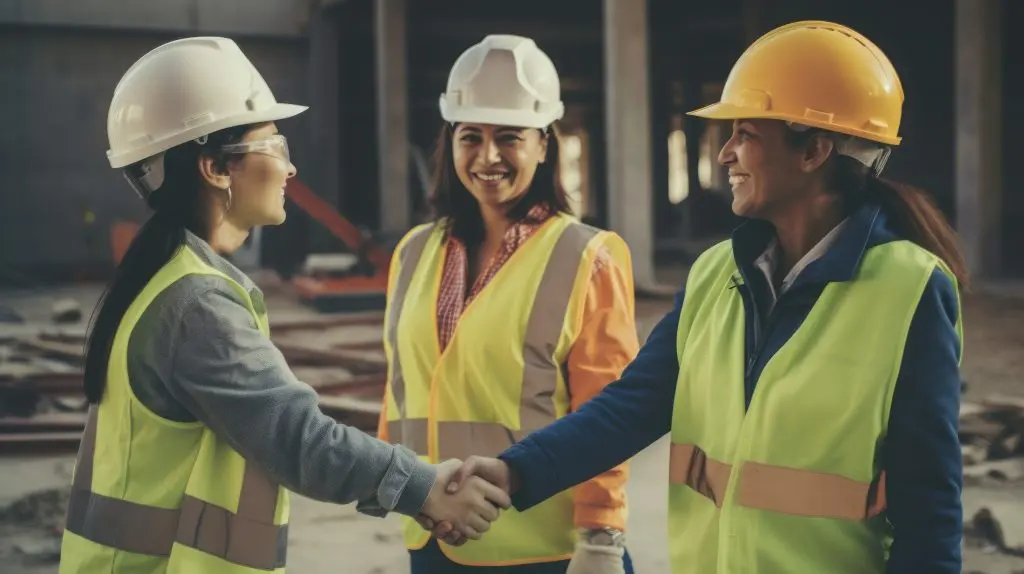
Toronto, ON – December 15, 2025 – The Canadian Wood Council (CWC) welcomes the announcement made today by the Honourable Tim Hodgson, Minister of Energy and Natural Resources, at the Toronto and Region Conservation Authority. The event celebrated funding for projects that strengthen Canada’s forestry sector and foster innovation in wood-based solutions. CWC received $8.5 million since 2023 to expand the use of wood-based products, broaden education on wood construction and contribute to the advancement of the National Building Code. The Canadian Wood Council deeply values the Government of Canada’s continued leadership in advancing innovative, low-carbon construction through the GCWood Program. This funding has allowed CWC and its WoodWorks program to support design and construction professionals with expert resources, tools, and guidance that help accelerate the adoption of wood construction nationwide. As we continue this work, we will help catalyze sustainable demand for construction solutions that are not only innovative but also replicable and rapidly deployed, approaches that will help address Canada’s housing and affordability challenges at scale. CWC and WoodWorks provide: project based technical assistance to architects, engineers, developers, and builders on wood design and construction; education and training through specialized programs, conferences, webinars, and resources developed for post-secondary students, tradespeople, and construction professionals to support advanced wood construction technologies including mass timber and engineered wood products; expert network development opportunities for industry professionals to connect and share best practices; and sector engagement in national code development to facilitate greater understanding and adoption of advanced, performance-based wood construction. “GCWood support enables us to provide critical technical advisory services, deliver wood-focused education and training to existing and future practitioners, and contribute to code developments that reflect the evolving strengths of modern wood products and systems. GCWood investments are important, strategic inputs that strengthen Canada’s forestry, manufacturing, and construction sectors. We look forward to building on our work to date as we engage with partners nationwide to accelerate the adoption of sustainable wood solutions and modern methods of construction.” – Rick Jeffrey, President and CEO, Canadian Wood Council. The Canadian Wood Council looks forward to collaborating with partners and stakeholders as these projects move forward, supporting Canada’s leadership in sustainable construction and forestry. Background The Canadian Wood Council received $4,999,536 to increase the use of wood-based solutions, systems, and products in Canada by building proficiency in the use of wood as a construction material through direct technical support, training, awareness, and networking. The Canadian Wood Council received $2,942,610 for a second project to increase the number of educational offerings and content related to wood construction education in order to increase the understanding and acceptance of wood as a building material by post-secondary students, trades and other construction industry professionals. The Canadian Wood Council received $594,000 for a third project to enable the forest industry’s participation over the next three years for code change proposals allowing for the increased use of low-carbon building materials and mass timber in wood buildings for the 2025 and 2030 editions of the National Building Code and to accelerate the adoption of performance-based building codes. About the Canadian Wood Council The Canadian Wood Council (CWC) is Canada’s unifying voice for the wood products industry. As a national federation of associations, CWC members represent hundreds of manufacturers across the country. CWC’s mission is to support its members by accelerating market demand for wood products and championing responsible leadership through excellence in codes, standards, and regulations. CWC also delivers technical support and knowledge transfer for the construction sector through its market leading WoodWorks program. About the National WoodWorks Program The Canadian Wood Council’s WoodWorks Program a national outreach initiative dedicated to advancing the use of wood in construction by providing educational opportunities and direct technical support. The program helps architects, engineers, developers and other industry professionals expand their capacity for wood design and construction, contributing to a more sustainable built environment.
Canadian Wood Council Joins Ontario’s Advanced Wood Construction Working Group

Toronto, ON – December 3, 2025 – The Canadian Wood Council (CWC) welcomes the Ontario government’s launch of the Advanced Wood Construction Working Group, a strategic team that will guide the implementation of Ontario’s Advanced Wood Construction Action Plan. The Working Group brings together leaders from across the manufacturing and construction sectors to identify practical ways to expand the use of Ontario-made wood products in homes, businesses, and communities across the province. “Ontario continues to show leadership in advancing innovative, low-carbon building solutions,” said Rick Jeffery, President and CEO of the Canadian Wood Council. “CWC looks forward to contributing technical expertise and national insight to help deliver on the Action Plan’s goals and grow advanced wood construction in Ontario.” As part of the Working Group, CWC will collaborate with government and industry partners to accelerate adoption of mass timber and prefabricated wood systems, support code modernization and training, and promote greater use of Ontario’s sustainable wood products in construction. “Building with wood offers a highly efficient solution for addressing Ontario’s housing needs while supporting the growth of local value-added manufacturing. More industrialized wood construction means more opportunities for skilled workers and their communities. I am proud to support Ontario’s leading role in the evolving construction sector, contributing to a more resilient, efficient, and forward-looking building environment.” Steven Street, Executive Director, WoodWorks Ontario, Canadian Wood Council. This initiative marks an important step forward in implementing Ontario’s Action Plan and driving investment, innovation, and housing solutions through advanced wood construction. About the Canadian Wood Council The Canadian Wood Council (CWC) is Canada’s unifying voice for the wood products industry. As a national federation of associations, our members represent hundreds of manufacturers across the country. Our mission is to support our members by accelerating market demand for wood products and championing responsible leadership through excellence in codes, standards, and regulations. We also deliver technical support and knowledge transfer for the construction sector through our market leading WoodWorks program.
Wood Design & Building Magazine, vol 24, issue 99

As the design and construction industry collectively strives towards a more sustainable built environment, one of the more interesting challenges in architecture today is how to work with what already exists. When existing structures are adapted and repurposed rather than demolished once they outlive their original use, resources are conserved, greenhouse gas emissions are lowered, heritage is preserved, and decarbonization goals are advanced. Whether it’s adapting a historic structure to a new use or extending the life of a contemporary one with a creative renovation or addition, designers are exploring the possibilities and finding ways to integrate wood into projects that build on the foundations of the past, figuratively and literally, to meet the needs of the present. In this issue, two feature stories explore different approaches to giving existing buildings new, expanded purpose. One project breathes new life into a traditional fieldstone barn through adaptive reuse, while another demonstrates how a lightweight mass timber vertical addition can expand an existing apartment building, adding new units to help meet growing housing needs. Both illustrate how wood enables design solutions that are respectful, efficient, and forward-looking. Projects like these remind us that innovation is a form of evolution, and sometimes, the most sustainable, creative, and community-minded choice is to work with what you’ve already got.
Mass Timber Business Case Studies

This document presents a series of business case studies that explore the financial performance of mass timber projects, providing quantitative data and qualitative insights to help developers and investors assess its economic viability. Each case study measures investment success, challenges, and lessons learned from the developer’s and project team’s perspectives. Moreover, by analyzing strategy, risk, revenue, cost and schedule, these case studies enable direct comparisons between mass timber and traditional construction methods. WoodWorks is seeking developers and owners with completed mass timber projects to share data for analysis, supporting education and training in the mass timber sector. The goal is to continuously expand case studies across various sectors and markets. To participate or learn more, please contact a WoodWorks staff member.
Canadian Wood Council’s WoodWorks Program Welcomes Rothoblaas Canada as National Partner
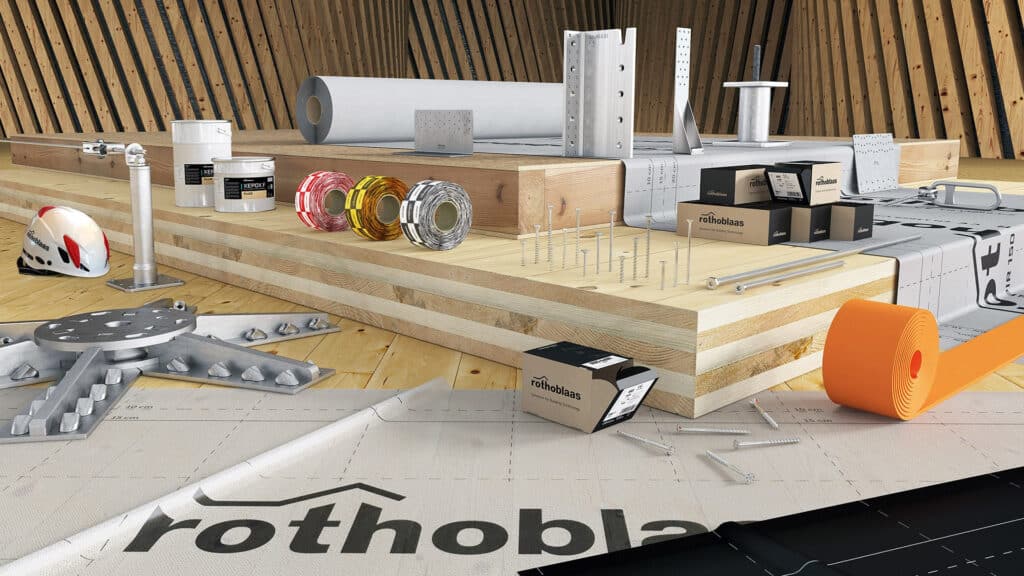

Ottawa, Ontario – October 16, 2025 — The Canadian Wood Council (CWC) is pleased to welcome Rothoblaas Canada as a new national partner of its WoodWorks program. This collaboration aligns two organizations committed to advancing wood construction across Canada through education, technical support, and strategic market development. As demand for high-performance, low-carbon buildings drives greater adoption of mass timber and other engineered wood systems, this partnership will strengthen the technical ecosystem supporting Canada’s construction industry. Leveraging Rothoblaas’s international leadership in structural connection technologies, envelope systems, and on-site safety solutions alongside WoodWorks’ national expertise in education, technical support, and market development, the collaboration will help advance best practices in timber design and construction. Together, the organizations will facilitate knowledge transfer and design innovation to support the integration of wood as a mainstream material in Canadian building projects. “For more than 20 years, WoodWorks has been delivering technical expertise and support to the professionals advancing wood construction across Canada. Partnering with this respected network allows Rothoblaas Canada to share our global engineering experience and help drive innovation in connection systems, building envelope performance, and safe, efficient timber assembly,” says François-Laurent Chabot, General Manager & Region Sales Manager for Rothoblaas Canada. “WoodWorks is proud to collaborate with Rothoblaas Canada to help build industry knowledge and acceptance of modern timber connection systems and other assembly solutions,” says Rick Jeffery, President and CEO of the Canadian Wood Council. “This partnership integrates Rothoblaas Canada’s expertise in engineered connectors and building envelope technologies with WoodWorks’ national platform for education and sector advancement—supporting a more seamless, performance-based approach to wood construction.” Through shared outreach, resource development, and technical education across the country, this national partnership aims to equip architects, builders, and developers with the knowledge they need to confidently design and build with wood. Broader adoption of wood solutions can play a pivotal role in meeting national housing and infrastructure goals, while contributing to Canada’s climate objectives and the transition to a low-carbon economy. About the Canadian Wood Council The Canadian Wood Council (CWC) is Canada’s unifying voice for the wood products industry. As a national federation of associations, our members represent hundreds of manufacturers across the country. Our mission is to support our members by accelerating market demand for wood products and championing responsible leadership through excellence in codes, standards, and regulations. We also deliver technical support and knowledge transfer for the construction sector through our market leading WoodWorks program. About the National WoodWorks Program The Canadian Wood Council’s WoodWorks Program a national outreach initiative dedicated to advancing the use of wood in construction by providing educational opportunities and direct technical support. The program helps architects, engineers, developers and other industry professionals expand their capacity for wood design and construction, contributing to a more sustainable built environment. About Rothoblaas Canada Rothoblaas Canada is a leading provider of innovative solutions for mass timber and wood construction, offering a comprehensive range of structural fasteners, connection systems, membranes, and safety products. As part of the global Rothoblaas group, the Canadian division supports architects, engineers, and builders with technical expertise and code-compliant solutions tailored to local needs. Through research, education, and collaboration, Rothoblaas Canada advances high-performance, sustainable construction and helps drive the growth of Canada’s wood building industry.
Canadian Wood Council’s WoodWorks Program Welcomes Nordic Structures as National Partner
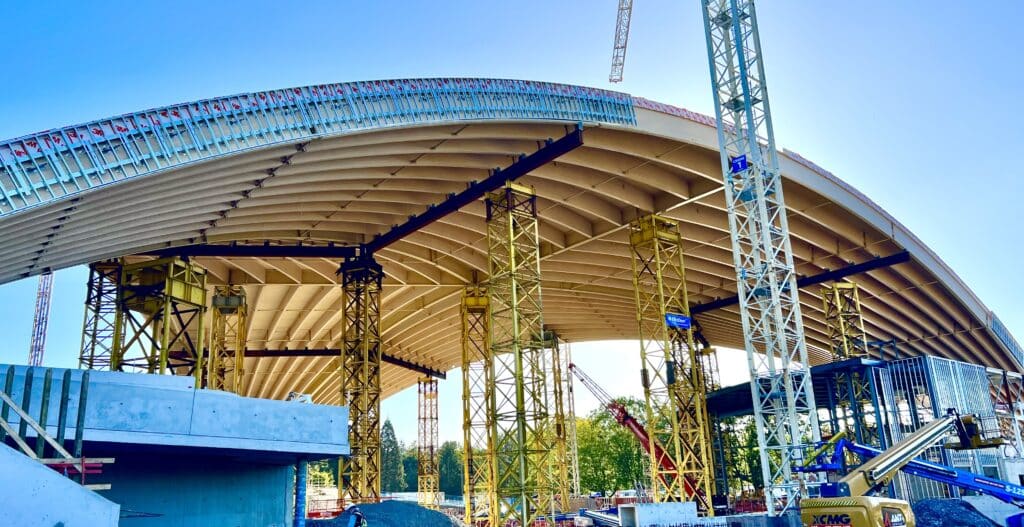

Ottawa, Ontario – October 14, 2025 — The Canadian Wood Council (CWC) is pleased to welcome Nordic Structures as a new national partner of its WoodWorks program. A longstanding Gold Level Sponsor of Cecobois (Centre d’expertise sur la construction commerciale en bois), WoodWorks’ sister organization in Quebec, Nordic Structures now joins WoodWorks as a partner at the national level. “Nordic Structures brings exceptional technical expertise and a deep commitment to responsible forest stewardship. Their collaboration with WoodWorks builds on years of leadership in Quebec and extends that impact nationally. By working together, we’re helping ensure that more communities across Canada can benefit from the innovation and environmental performance that wood construction delivers. “ says Rick Jeffery, President & CEO of the Canadian Wood Council. “Building on our valued relationship with Cecobois, we are excited to partner with WoodWorks to advance the knowledge, innovation, and adoption of engineered wood products as a structural solution across Canada,” said David Croteau, Nordic Structures, Vice-President, Operations and Engineering. As we look to the future, partnerships like this are vital to expanding the adoption of structural wood solutions that can meet Canada’s growing demand for affordable housing and resilient infrastructure. Nordic’s leadership in design, engineering, and manufacturing—combined with the technical expertise of WoodWorks—will help unlock new opportunities for high-performance, low-carbon buildings across every region of the country. About the Canadian Wood Council The Canadian Wood Council (CWC) is Canada’s unifying voice for the wood products industry. As a national federation of associations, our members represent hundreds of manufacturers across the country. Our mission is to support our members by accelerating market demand for wood products and championing responsible leadership through excellence in codes, standards, and regulations. We also deliver technical support and knowledge transfer for the construction sector through our market leading WoodWorks program. About the National WoodWorks Program The Canadian Wood Council’s WoodWorks Program a national outreach initiative dedicated to advancing the use of wood in construction by providing educational opportunities and direct technical support. The program helps architects, engineers, developers and other industry professionals expand their capacity for wood design and construction, contributing to a more sustainable built environment. Nordic Structures Nordic Structures offers engineered wood products and comprehensive technical services to enable state-of-the-art mass timber projects. Nordic’s founding company, Chantiers Chibougamau, responsibly harvests black spruce from Northern Quebec’s boreal forest and transforms the raw material into a full catalog of wood-based products, from I-joists to both industrial and architectural grades of glulam and CLT. Collaborating with architects, engineers, and construction firms, the team has delivered successful results on thousands of mass timber projects spanning all major sectors of public life.
Catherine Lalonde Memorial Scholarships

Call for Submissions: 2025 Catherine Lalonde Memorial Scholarships for Wood Related Research Catherine Lalonde Memorial Scholarships are presented to graduate students, enrolled at Canadian Universities, who demonstrate excellence in their studies of structural wood products or wood design. The Canadian Wood Council (CWC) invites submissions from graduate students in engineering, architecture, and wood science. Submitted projects must demonstrate their value and impact on Canadian-made structural wood products and/or their role in advancing domestic wood construction. The CWC will award two scholarships to graduate students whose outstanding wood research not only demonstrates academic excellence but also mirrors the unwavering passion for the wood industry exemplified by Catherine Lalonde, in whose honor the scholarships are named. Catherine, a professional engineer, was a passionate representative of our industry who relentlessly championed the use of wood in residential and commercial construction during her 10 years with the CWC. She served as president of the CWC from 2000 until 2003 when she tragically lost her battle with cancer. This award was established to commemorate Catherine’s memory and perpetuate the legacy of excellence and advocacy she bestowed upon the Canadian wood products industry throughout her influential tenure at the CWC. Scholarship Details and Application Process 1. Scholarship Value Two scholarships, valued at $3,000 each, will be awarded to outstanding graduate students. 2. Who can apply? Students enrolled in graduate programs in engineering, architecture, or wood science whose work contributes to the advancement of domestic wood products and construction. 3. Application Process Step Requirement Deadline Step 1 – Notification of Interest The Notification of Interest submission period has now closed. Eligible applicants have been notified of their preselection via email. If you were unable to submit your Notification of Interest before the deadline for reasons beyond your control and expect to complete the full application on time, please contact Ioana Lazea at ilazea@cwc.ca to discuss your situation. Closed – October 17, 2025 Step 2 – Full Application Submission Preselected applicants have been invited to complete the Full Application through a dedicated portal and upload all required documents (see checklist below). November 14, 2025 4. Full Application Submission Checklist For Step 2, applicants must upload the following documents to the submission portal: One cover letter. Official transcripts: Master’s applicants: undergraduate and graduate transcripts. Doctoral applicants: master’s transcript. Two-page description of the project, plus up to two pages of drawings or photos (if applicable). Two letters of reference, preferably from faculty members or supervisors familiar with the applicant’s work. For additional information, please contact Ioana Lazea at ilazea@cwc.ca
Acoustic Comparative Study

In a context where wood construction is gaining momentum, acoustics remains a key challenge in ensuring occupant comfort and compliance with standards. With this in mind, AcoustiTECH, an expert in acoustic solutions, has partnered with FPInnovations, a leader in research and development in the wood sector, to conduct an in-depth comparative study in its laboratory facility. Who We Are AcoustiTECH is a broker specializing in acoustic solutions, supporting building professionals in selecting highperformance materials that meet and exceed industry standards. With 25 years of experience and unique expertise, we offer customized assemblies through a specialized brand ecosystem and reliable data. Our personalized service, backed by dedicated technical and engineering teams, ensures tailored and effective solutions that enhance the acoustic comfort of occupants. FPInnovations is a globally recognized, private, non-profit organization specializing in research and development for the forestry sector. Its mission is to support businesses and building professionals in innovating and optimizing wood-based materials. With ISO 17025-accredited laboratories and state-of-the-art facilities, FPInnovations assesses the performance of wood structures in terms of acoustics, vibrations, fire resistance, and more. Study Objective At AcoustiTECH, our goal is to continuously innovate by delivering new data and acoustic solutions tailored to the specific requirements of each project. This collaboration with FPInnovations marks a significant milestone in our acoustic analysis of wood structures, as it represents our first large-scale data collection on a GLT masstimber slab and our second mass-timber campaign overall, building on a prior study. Through this study, we obtain precise acoustic measurements for this structural system and conduct rigorous comparisons across numerous innovative market solutions. We take into account key project criteria such as acoustic performance, budget, thickness, weight, and even design, as different acoustic solutions can also influence the choice of floor coverings. Grounded in a scientific approach and conducted in controlled environments with FPInnovations, this research aims to evaluate various acoustic configurations optimized for mass timber construction. By combining technical expertise, innovation, and in-depth analysis, we provide architects, engineers, and developers with high-performance solutions that meet and exceed the industry standards.
Wood Design & Building Award Winning Projects Announced

Vancouver, BC – September 23, 2025 – The Canadian Wood Council is pleased to announce the winning projects of the 41st annual Wood Design & Building Awards program. This prestigious awards program recognizes and celebrates the outstanding work of architectural professionals from Canada and around the world for excellence in wood design and construction. “The diversity and creativity in this year’s winning projects demonstrate how wood can connect people with nature,” says Martin Richard, Vice President of Communications and Market Development at the Canadian Wood Council (CWC). “These designs not only showcase wood’s versatility, but also create spaces that enrich daily life and support community well-being. They are high-performance solutions that respond to today’s urgent need for housing, schools, and community spaces.” “It’s a delight each year to see the latest and greatest wood buildings nominated to our awards program and it’s a privilege to recognize the best projects from the impressive submissions we receive,” added Ioana Lazea, Senior Project Manager at CWC responsible for delivering the awards program. “This year’s competition drew a remarkable 140 entries. We are deeply grateful to our esteemed jurors for the significant effort they invested in reviewing each one and for their careful deliberations in selecting the winners.” 18 projects earned recognition from the Wood Design & Building Awards jury. The jurors for the Wood Design & Building Awards were: Omar Ghandi, Principal at Omar Ghandi Architects Jane Abbott, Partner at Abbott Brown Architects Alec Holser, Founding Principal at Opsis Architecture 14 additional projects were selected for recognition under the WoodWorks category of the Wood Design Awards programs which have regional competitions in BC, Ontario, and the Prairie provinces for projects located in those jurisdictions. The jurors for the WoodWorks Awards category were: Eric Karsh, Founding Partner of Equilibrium Brenda Izen, Founding Principal at Izen Architecture Carol Belanger, City Architect, Edmonton In total, 38 projects from Canada and around the world were honoured at the Wood Design and Building Awards celebration hosted Tuesday, September 23, 2025, at the Woodrise Conference in Vancouver, BC. COMPLETE LIST OF AWARD-WINNING PROJECTS FOLLOWS: Honor The Spirit Garden (Toronto, ON) | Gow Hastings Architects in collaboration with Two Row Architects Fraser Mills Presentation Centre (Coquitlam, BC) | Patkau Architects Pacific Northwest Residence (Washington State) | Cutler Anderson Architects Google Borregas (Sunnyvale, CA, USA) | Project Designer: MGA | Michael Green Architecture, Architect of Record: SERA Architects TRUMPF Education Center (Ditzingen, Germany) | Barkow Leibinger Dwelling on the Mountainside: Jiuceng Art Gallery (Lishui, Zhejiang Province, China) | Atelier Lu+Architects Merit Vesterheim Commons (Decorah, IA, USA) | Snøhetta DogTrot Magnetawan (Magnetawan, ON) | Williamson Williamson Aiken Audubon Research Outpost (Chico Basin Ranch, CO, USA) | ColoradoBuildingWorkshop at CU Denver Citation Walking Dunes (Amagansett, NY, USA) | Bates Masi + Architects Timbrelyn (Bethel, NY 12720, USA) | Adel Research Group (ARG) sʔitwənx Child Care (Kelowna, BC) | Public Architecture + Design Canadian Canoe Museum (Peterborough, ON) | Unity Design Studio Greenhill School, Rosa O. Valdes STEM + Innovation Center (Addison, TX, USA) | Bohlin Cywinski Jackson Upper Canada College – Lindsay Boathouse (Toronto, ON) | VJAA Inc. (Lead Design Architect) | RDHA (Architect of Record) Winthrop Library (Winthrop, WA, USA) | Johnston Architects (Architect of Record) and Prentiss Balance Wickline Architects (Associate Architect) Toronto and Region Conservation Authority Headquarters (Toronto, ON) | Bucholz McEvoy Architects + ZAS Architects and Interiors MUMO (Museum of Motorcycle) (Puerto Octay, North Patagonia, Chile) | DRAA Sansin Sponsored Award Google Borregas (Sunnyvale, CA, USA) | Project Designer: MGA | Michael Green Architecture, Architect of Record: SERA Architects Sustainable Forestry Initiative Sponsored Awards Wahta’ elementary school (Wendake, QC) | DG3A Architecture Kreher Preserve & Nature Center Environmental Education Building (Auburn, AL, USA) | Leers Weinzapfel Associates Architects, Inc. Western Red Cedar Sponsored Awards San Juan Islands Residence (Eastsound, WA) | Vandervort Architects The Granary at Southlands (Delta (Tsawwassen) – BC) | MOTIV Architects Wood Preservation Sponsored Award Catchacoma Cottage (The Kawarthas, Municipality of Trent Lakes, ON) | Dubbeldam Architecture + Design WoodWorks Ontario Wood Design Awards DogTrot Magnetawan (Magnetawan, ON) | Williamson Williamson Ontario Secondary School Teachers’ Federation (OSSTF) Headquarters and Multi-Tenant Complex (Toronto, ON) | Moriyama Teshima Architects Toronto and Region Conservation Authority Headquarters (Toronto, ON) | Bucholz McEvoy Architects + ZAS Architects and Interiors Upper Canada College – Lindsay Boathouse (Toronto, ON) | VJAA Inc. (Lead Design Architect) | RDHA (Architect of Record) 1120 Ossington (Toronto, ON) | mcCallumSather WoodWorks BC Wood Design Awards Fraser Mills Presentation Centre (Coquitlam, BC) | Patkau Architects Adams Lake Health + Wellness Centre (Chase, BC) | Unison Architecture Ltd. Kin Park Pavilion and Ice Rink (Fort St. John, BC) | Public Architecture + Design sʔitwənx Child Care (Kelowna, BC) | Public Architecture + Design Point Grey House (Vancouver, BC) | Patkau Architects WoodWorks Prairie Wood Design Awards F Residence (RM of Stanley, MB) | 1×1 architecture inc. Riel Construction Office, (Dugald, MB) | Republic Architecture Inc. Sam Centre (Calgary, AB) | Diamond Schmitt Architects G7 Summit – Interior Renovations (Kananaskis, AB) | 1×1 architecture VIEW A VIDEO COMPILATION OF THIS YEAR’S WINNERS HERE: https://cwc.ca/WoodDesignandBuildingAwards2025/ FOR MORE INFORMATION, PLEASE CONTACT: Sarah Hicks Communications Manager, Canadian Wood Council 1-705-796-3381 | shicks@cwc.ca
Canadian Wood and Forestry Resources

National Provincial Canadian Wood Council WoodWorks Forest Products Association of Canada Certification Canada Mass timber road map Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada Forest sector funding programs The Canadian Forest Service Canada Action – Forestry Industry in Canada FPInnovations Forest Enhancement Society of BC Province of British Columbia – Ministry of Forests British Columbia, Forestry Innovation Investment Mass Timber Demonstration Program in British Columbia Alberta Forest Products Association Ontario Forest Industries Association Ontario Wood Cecobois Conseil de l’industrie forestière du Québec Maritime Lumber Bureau Government Resources Invest in Canada – Services The State of Canada’s Forests Annual Report Canadian Forests – Federal Government Mass Timber Action Plan Trade Commissioner Service Forestry and wood products Funding and financing for international business Opportunities for Wood (PDF) Two Sides – Canadian forests are a renewable natural resource Canadian Council of Forest Ministers – Healthy forests. Healthy communities. naturally:wood – Mass Timber Demonstration Program The State of Canada’s Forests Annual Report 2023 (.pdf) The Conference Board of Canada – Use of Forest Resources COFI – Forest Facts