Bolts are widely used in wood construction. They are able to resist moderately heavy loads with relatively few connectors.
Bolts may be used in wood-to-wood, wood-to-steel and wood-to-concrete connection types. Some typical structural applications for bolts include:
- purlin to beam connections
- beam to column connections
- column to base connections
- truss connections
- timber arches
- post and beam construction
- pole-frame construction
- timber bridges
- marine structures
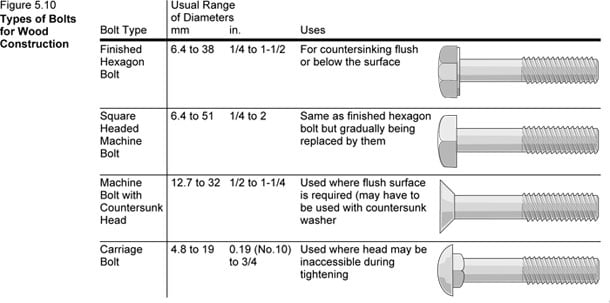
Several types of bolts as shown in Figure 5.10 below, are used for wood construction with the hexagon head type being the most common. Countersunk heads are used where a flush surface is desired. Carriage bolts can be tightened by turning the nut without holding the bolt since the shoulders under the head grip the wood.
Bolts are commonly available in imperial diameters of 1/4, 1/2, 5/8, 3/4, 7/8 and 1 inch. Bolts are installed in holes drilled slightly (1 to 2 mm) larger than the bolt diameter to prevent any splitting and stress development that could be caused by installation or subsequent wood shrinkage. Depending on the diameter, bolts are available in lengths from 75 mm (3″) up to 400 mm (16″) with other lengths available on special order.
Bolts can be dipped or plated, at an additional cost, to provide resistance to corrosion. In exposed conditions and high moisture environments, corrosion should be resisted by using hot dip galvanized or stainless steel bolts, washers and nuts.
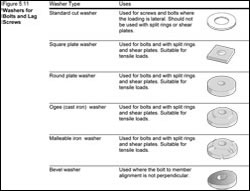
Washers are commonly used with bolts to keep the bolt head or nut from crushing the wood member when tightening is taking place. Washers are not required with a steel side plate, as the bolt head or nut bears directly on the steel. Common types of washers are shown in Figure 5.11 below.
Design information provided in CWC’s Wood Design Manual is based on bolts conforming to the requirements of ASTM A307 Standard Specification for Carbon Steel Bolts, Studs, and Threaded Rod 60 000 PSI Tensile Strength or Grade 2 bolts and dowels as specified under SAE J429 Mechanical and Material Requirements for Externally Threaded Fasteners.